Contents of the powerpoint on Tablets aqeuos film coating include:
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
AQUEOUS FILM COATING OF DOSAGE FORM
Film formation mechanism
Film formers
Plasticizers and colours
PROCESS PARAMETERS
HOW THE COATING PROCESS WORKS
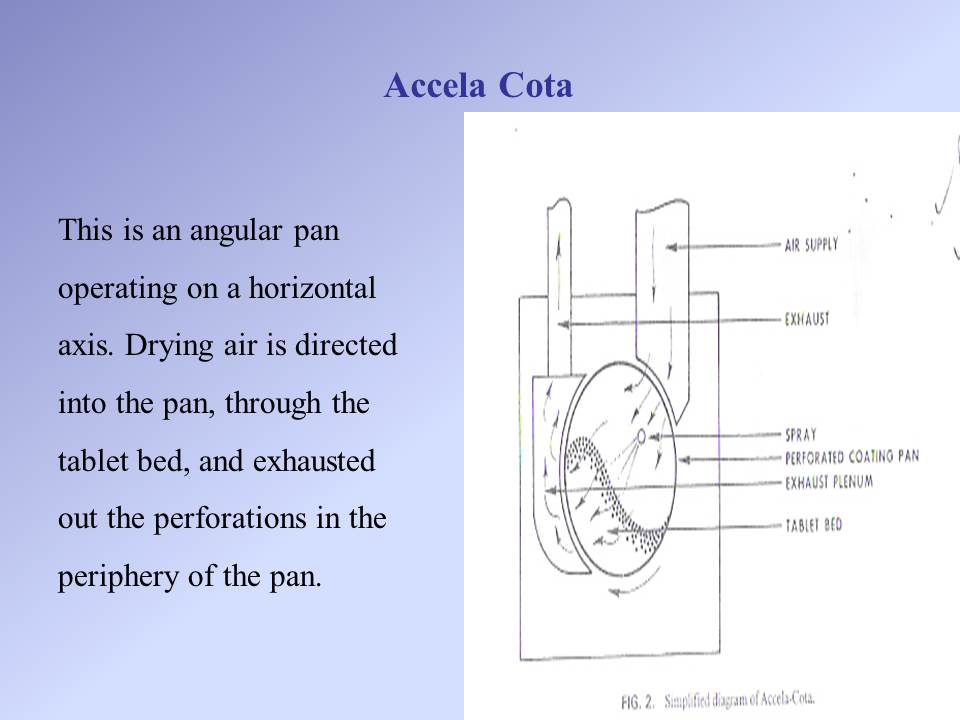
COATING EQUIPMENTS
COATING DEFECTS
SOLVENT FILM COATING
COATING:
IT is the application of coating composition on to the moving bed of tablets with concurrent use of heated air to facilitate evaporation of the solvent.
Formation of films from aqueous polymeric dispersions
This requires the coalescence of polymer particles into a continuous film.
This process involves:
Rapid evaporation of water, causing the particles of dispersed polymer to be brought into close contact with one polymer.
Development of pressures (associated with capillary forces within the structure) that overcome repulsive forces between particles and cause deformation of the polymer particles.
Gradual coalescence of the polymer particles as a result of viscous flow and movement of polymer molecules across the interfaces between particles.
Aqueous polymeric dispersions must be processed at temperatures in excess of the
glass-transition temperature of the polymer.
Download the powerpoint by liking us on Facebook
[like-gate][/like-gate]
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3547″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PPT here[/button]
You can also download the PDF onTablets aqeuos film coating by clicking here
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3547″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PDF here[/button]