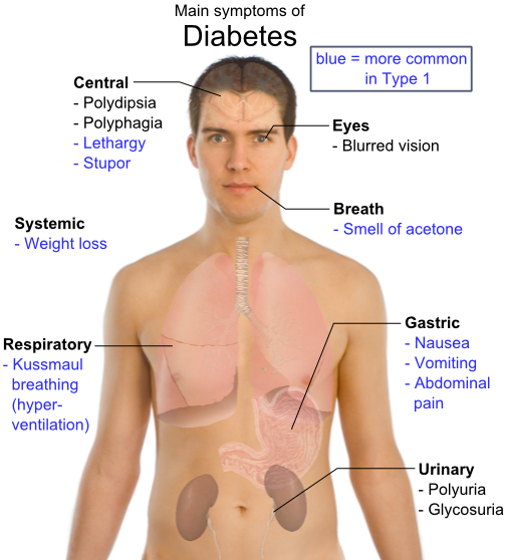
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes—is a condition in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. Diabetes mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia glycosuria, hyperlipemia, negative nitrogen balance and sometimes ketonemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both.
This high blood sugar produces the classical symptoms of polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia (increased thirst) and polyphagia (increased hunger).
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes: results from the body’s failure to produce insulin, and presently requires the person to inject insulin.
Type 2 diabetes: results from insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to use insulin properly, sometimes combined with an absolute insulin deficiency.
Gestational diabetes: is when pregnant women, who have never had diabetes before, have a high blood glucose level during pregnancy.
Diagnosis
EPIDIMEOLOGY:
There is an increase in the prevalence of type 1diabetes also, but main cause of diabetic epidemic is type2 diabetes mellitus, which accounts for more than 90 percent of all diabetes cases. According to World Health Organization (WHO) reports, India had 32 million diabetic people in the year 2001. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimates the total number of diabetic subjects to be around 40.9 million in India and this is further set to rise to 69.9 million by the year 2025. The majority of cases of diabetes fall into two broad etiopathogenetic categories now called type 1 and T2 DM. The etiologic classification of diabetes mellitus currently recommended by WHO and the ADA in 1997.
ORAL HYPOGYCEMIC DRUGS
Biguanide Metformin
Sulfonylureas Glimepiride,gliclazide,glipizide,glyburide,glibenclamide
Meglitinides Repaglinide,nateglinide
Gliptins (DPP-4 inhibitors) Sitagliptin,vildagliptin,saxagliptin,alogliptin,linagliptin
Thiazolidinediones (PPAR-γ agonists) Pioglitazone,rosiglitazone
α-Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose,miglitol,voglibose
Dopamine D2-receptor agonists Bromocriptine
SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
Insulin Rapid, short, intermediate, and long-acting formulations.
Newer insulins Insulin detemir, insulin glulisine, insulin degludec
GLP-1 agonists Exenatide, liraglutide,albiglutide,lixisenatide,taspoglutide
Amylin analogue Pramlintide
RECENT DRUGS
Sodium–glucose-cotransporter-2 (SGL2) inhibitors
Dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, ASP1941, LX4211, and BI10773
11β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase-1 inhibitors
INCB13739 (200 mg) DUAL PPAR (γ +α) AGONIST
Aleglitazar Glucokinase activator Piragliatin, compound 14,
R1511, AZD1656, AZD6370, compound 6 Bile acid sequestrants Colesevelam
Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody Otelixizumab, teplizumab Cannabinoid receptor-1 antagonists
Rimonabant Histamine H3 receptor agonist Proxyfan
Glucagon receptor antagonists Compound 1 (cpd 1)
Atherogenics antioxidant/vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
Succinobucol/AGI 1067
Recombinant human glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 (rhgad65) Vaccine, induces immunotolerization IL-1 antagonist
Anakinra Insulin action enhancers
Gip antagonists Sirtuins
Adipose tissue signals