In this article we provide vital information about Uterus. If you want to know how your uterus is then this is the place to read. You van see Uterus Function Anatomy Location Pictures of UTERUS. Uterus in Child, Uterus at Menopause and Uterus at Pregnancy are given clearly.
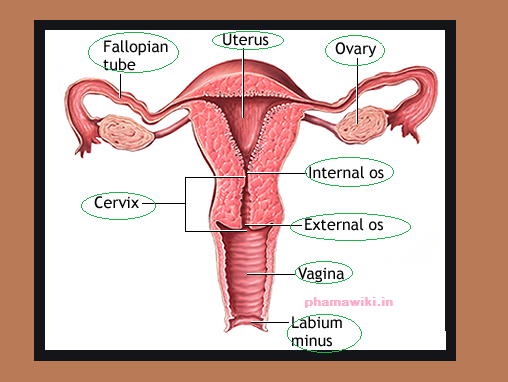
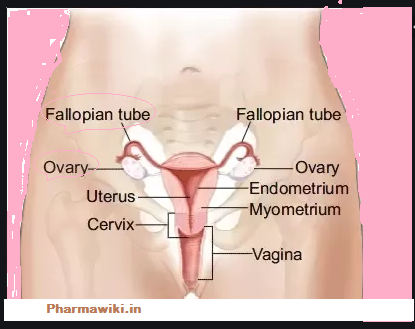
Uterus Anatomy Pictures:
Uterus in the Child:
The fundus and body of the uterus remain small until puberty, when they enlarge greatly in response to the estrogens secreted by the ovaries.
Uterus after Menopause:
After menopause, the uterus atrophies and becomes smaller and less vascular. These changes occur because the ovaries no longer produce estrogens and progesterone.
Uterus in Pregnancy:
During pregnancy, the uterus becomes greatly enlarged as a result of the increasing production of estrogens and progesterone, first by the corpus luteum of the ovary and later by the placenta. At first, it remains as a pelvic organ, but by the third month the fundus rises out of the pelvis, and by the ninth month it has reached the xiphoid process. The increase in size is largely a result of hypertrophy of the smooth muscle fibers of the myometrium, although some hyperplasia takes place. Role of the Uterus in Labor Labor, or parturition, is the series of processes by which the baby, the fetal membranes, and the placenta are expelled from the genital tract of the mother. Normally, this process takes place at the end of the 10th lunar month, at which time the pregnancy is said to be at term. The cause of the onset of labor is not definitely known. By the end of pregnancy, the contractility of the uterus has been fully developed in response to estrogen, and it is particularly sensitive to the actions of oxytocin at this time. It is possible that the onset of labor is triggered by the sudden withdrawal of progesterone. Once the presenting part (usually the fetal head) starts to stretch the cervix, it is thought that a nervous reflex mechanism is initiated and increases the force of the contractions of the uterine body. The uterine muscular activity is largely independent of the extrinsic innervation. In women in labor, spinal anesthesia does not interfere with the normal uterine contractions. Severe emotional