Paracetamol Dosage By Weight Child
The correct dose of paracetamol for a child depends on their weight. The usual dose is 15 mg per kilogram of weight. In other words, if a baby weighs 10 kg it should have 10 x 15mg, which is 150 mg. This dose can be taken once every 4 to 6 hours, up to 4 times in 24 hours if needed.
Maximum Dose Of Paracetamol For Child
For children without underlying medical conditions, or with underlying medical conditions that are not inflammatory in nature, beginning treatment with oral paracetamol is preferred because of its long track record of safety.
The correct dose of paracetamol for a child depends on their weight. The usual dose is 15 mg per kilogram of weight.
You should not exceed the recommended dose except on the advice of your doctor. No child should take a total of more than 60 mg per kilogram of their body weight in a day.
Paracetamol tablet dosage for 10 year old:
Example of calculating a paracetamol dose:
A boy, aged 10 years, weighing 67 kg presents with myalgia of a suspected viral cause. You prescribe paracetamol for management at home. The calculation for paracetamol dosing is 15 mg × 67 kg = 1005 mg , however, you round this down to the maximum adult dose of 1 g, which is prescribed as 20 mL of a 250 mg/5 mL formulation, every four to six hours with no more than four doses every 24 hours.
Paracetamol Dosage Weight Calculator
Paracetamol is a medicine that is commonly used in children and adults which is available without a prescription. The main uses of paracetamol are for relief of pain and for reducing a fever.
Paracetamol Dosage By Weight Adults
Paracetamol Side Effects:
Paracetamol is one of the most commonly used ‘over-the-counter’ medicines, especially for the minor illnesses suffered by many children. But it is not always used in the correct dosage, which may make it less effective or dangerous.
Reasons Side Effects with paracetamol included:
- Exceeding recommended doses
- Too frequent dosing
- Prolonged dosing (up to 24 days in one case)
Paracetamol rarely causes side-effects when it is taken as recommended, but if you experience any symptoms which you think may be due to it, discuss them with your pharmacist or doctor.
Paracetamol Contraindications:
Paracetamol overdose can result in liver damage and, at very high dosages, can be fatal.
Some people need to take extra care with paracetamol. Like :
If you have had an allergic reaction to paracetemol or any other medicines in the past
If you have liver or kidney problems
If you regularly drink more than the maximum recommended amount of alcohol (14 units a week)
If you take medicine for epilepsy
If you take medicine for tuberculosis (TB)
If you take the blood-thinner warfarin and you may need to take paracetamol on a regular basis
Paracetamol Indication:
Too much paracetamol is very harmful to the liver.
If you realise you have had too much (including other products with paracetamol in it), call your doctor, nurse or the Poisons Centre 0800 POISON (0800 764 766) immediately.
Older people are most at risk so take extra care.
Do NOT wait for signs of an overdose as these appear late when the damage to the liver is already done.
Late signs may include:
- nausea or vomiting
- diarrhoea,
- yellow skin or eyes,
- poor appetite,
- confusion or extreme sleepiness.
paracetamol dosage weight calculator:
Maximum dose of paracetamol for Adults:
Do not take more than 4 grams in 24 hours. This equates to 8 x 500 mg tablets, or 6 X 665 mg tablets per day.
Keep track of the timing of the doses and check when it was last taken before taking it again.
Paracetamol tablet dosage for children:
The oral dose of paracetamol for children aged 1 month to 18 years is:
15 mg/kg per dose, to a maximum of 1 g per dose, every four to six hours, with a maximum of 60 mg/kg daily, without exceeding 4 g daily
paracetamol dosage by weight adults
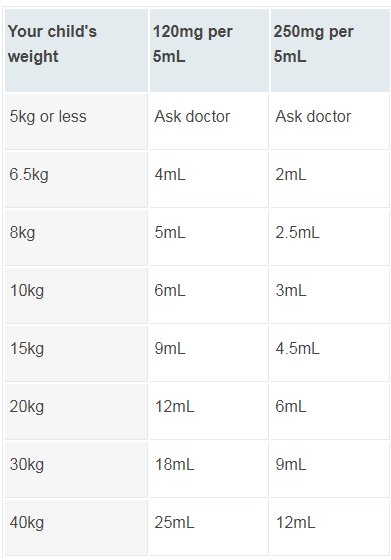
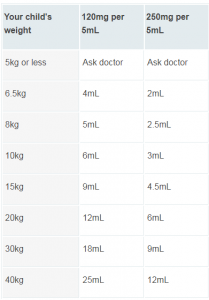
Paracetamol Dosage for Infants:
For children aged 6 months-1 year: 120 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
For children aged 3-5 months: 60 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
For children aged 2 months following immunization: 60 mg, repeated once after 4-6 hours if needed.
Paracetamol Dosage for Toddlers:
For children aged 2-3 years: 180 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
For children aged 6 months-1 year: 120 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
Paracetamol Uses:
Paracetamol is Used for Pain and fever (high temperature) in adults and children. Available as Tablet, capsule, soluble tablet, ‘melt-in-the-mouth’ tablet, oral liquid, oral liquid sachets, suppository and injection
FOR MORE DETAILS OF USES OF PARACETAMOL CLICK
Paracetamol 500mg Dosage
Generally 3 times a day or 500 mg 6hrs
Paracetamol Dosage For 12 Year Old
Paracetamol Dosage Calculator Adults:
The usual dose in adults is 500 mg to 1 gram (1 or 2 tablets) every 4 to 6 hours when required for pain.
Paracetamol can be safely used by adults including pregnant women but there is a limit to the amount of paracetamol that can be safely taken in a 24-hour period. Taking more than the daily limit is very harmful to the liver. For adults the usual maximum dose is 4 grams per day. This may be less if you are frail or elderly.
Paracetamol tablets are available in two strengths — 500 mg tablets or 665 mg tablets.
The 665 mg tablets are used for osteoarthritis
Paracetamol 500mg
Paracetamol is used for relief of pain and Fever. Analgesic and Anti Pyretic. Paracetamol has analgesic (pain relief) and antipyretic(reduces fever) but no anti-inflammatory activity; it is less irritant to the stomach than Ibuprofen.
It will not cause drowsiness or cause your child to sleep. It can be used for children and babies over 3 months old. Younger babies must see the doctor.
Paracetamol is highly lipid-soluble and has a relatively short half life of 2–2.5 hours.2 Following oral administration, paracetamol is rapidly absorbed across the mucosa of the duodenum and into the bloodstream where it is mainly metabolised by the liver.
Paracetamol Dosage By Weight Child Adult pdf
Recommended doses of paracetamol are:
- For adults and children aged 16 years and older: 500 mg-1 g every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of 4 g daily.
- For children aged 12-15 years: 480-750 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 10-11 years: 480-500 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 8-9 years: 360-375 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 6-7 years: 240-250 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 4-5 years: 240 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 2-3 years: 180 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 6 months-1 year: 120 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 3-5 months: 60 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
- For children aged 2 months following immunization: 60 mg, repeated once after 4-6 hours if needed.
Paracetamol Tablet
Food Interactions to Paracetamol: 🙄
Avoid alcohol (may increase risk of hepatotoxicity).
Take without regard to meals.
Pharmacodynamics of Paracetamol: 😆
Acetaminophen (USAN) or Paracetamol (INN) is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic drug that is used for the relief of fever, headaches, and other minor aches and pains. It is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications and many prescription analgesics. It is extremely safe in standard doses, but because of its wide availability, deliberate or accidental overdoses are not uncommon. Acetaminophen, unlike other common analgesics such as aspirin and ibuprofen, has no anti-inflammatory properties or effects on platelet function, and it is not a member of the class of drugs known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs. At therapeutic doses acetaminophen does not irritate the lining of the stomach nor affect blood coagulation, kidney function, or the fetal ductus arteriosus (as NSAIDs can). Like NSAIDs and unlike opioid analgesics, acetaminophen does not cause euphoria or alter mood in any way. Acetaminophen and NSAIDs have the benefit of being completely free of problems with addiction, dependence, tolerance and withdrawal. Acetaminophen is used on its own or in combination with pseudoephedrine, dextromethorphan, chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, codeine, hydrocodone, or oxycodone.
Pharmacology and Mechanism of action of Paracetamol:
Acetaminophen is thought to act primarily in the CNS, increasing the pain threshold by inhibiting both isoforms of cyclooxygenase, COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 enzymes involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. Unlike NSAIDs, acetaminophen does not inhibit cyclooxygenase in peripheral tissues and, thus, has no peripheral anti-inflammatory affects. While aspirin acts as an irreversible inhibitor of COX and directly blocks the enzyme’s active site, studies have found that acetaminophen indirectly blocks COX, and that this blockade is ineffective in the presence of peroxides. This might explain why acetaminophen is effective in the central nervous system and in endothelial cells but not in platelets and immune cells which have high levels of peroxides. Studies also report data suggesting that acetaminophen selectively blocks a variant of the COX enzyme that is different from the known variants COX-1 and COX-2. This enzyme is now referred to as COX-3. Its exact mechanism of action is still poorly understood, but future research may provide further insight into how it works. The antipyretic properties of acetaminophen are likely due to direct effects on the heat-regulating centres of the hypothalamus resulting in peripheral vasodilation, sweating and hence heat dissipation.
Paracetamol Structure
paracetamol 125 mg dosage
Paracetamol dosage for 12 year old
Paracetamol dose for children aged 12-15 years: 480-750 mg every 4-6 hours up to a maximum of four doses daily.
Clear your Doubts : Frequently Asked Questions on Paracetamol
Given the number of questions, I’ll provide detailed answers in sections to keep the content manageable. Let’s start with General Information and Dosage and Administration:
General Information
- What is paracetamol used for?
Paracetamol is primarily used to relieve mild to moderate pain (e.g., headaches, muscle pain, and toothaches) and to reduce fever. It is often used as a safer alternative to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief and fever reduction. - Is paracetamol the same as acetaminophen?
Yes, paracetamol is the same as acetaminophen. “Paracetamol” is commonly used in countries like the UK and India, while “acetaminophen” is the term used in the US and Canada. Both refer to the same chemical compound. - What are the common brand names of paracetamol?
Common brand names include:- Tylenol (US/Canada)
- Panadol (Worldwide)
- Crocin (India)
- Calpol (India/UK)
- How does paracetamol work in the body?
Paracetamol works by blocking the production of prostaglandins in the brain. Prostaglandins are chemicals that cause pain and fever. Unlike NSAIDs, it does not reduce inflammation significantly.
Dosage and Administration
- What is the recommended dose of paracetamol for adults?
- Standard dose: 500–1000 mg every 4–6 hours.
- Maximum dose: 4000 mg (4 grams) per day, unless directed by a doctor.
- Can I take paracetamol on an empty stomach?
Yes, paracetamol can be taken on an empty stomach as it is gentle on the stomach lining. However, if you experience discomfort, you may take it with food or milk. - What is the maximum daily dose of paracetamol?
The maximum daily dose for an adult is 4000 mg (4 grams), taken in divided doses. Exceeding this amount can lead to liver damage. - How often can I take paracetamol?
You can take paracetamol every 4–6 hours, but do not exceed the maximum dose of 1000 mg per dose or 4000 mg in 24 hours. - What happens if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one. Do not double your dose to make up for the missed dose.
Safety and Side Effects
- What are the side effects of paracetamol?
Paracetamol is generally well-tolerated, but some side effects can occur, including:
- Rare allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Liver damage or failure (in cases of overdose or prolonged use)
- Low blood pressure or rapid heartbeat (very rare)
Severe side effects are uncommon when taken at the recommended dose.
- Can paracetamol cause liver damage?
Yes, paracetamol can cause liver damage if taken in doses exceeding the recommended daily limit (4000 mg for adults). Chronic alcohol use or pre-existing liver conditions can increase the risk even at lower doses. - Is paracetamol safe for children and infants?
Yes, paracetamol is safe for children and infants when used as directed. Dosage is based on the child’s weight and age. Pediatric formulations (e.g., syrup) usually include a dosing guide. Always consult a doctor for proper dosing. - Can pregnant or breastfeeding women take paracetamol?
Paracetamol is considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding when taken as directed. However, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider before use. - What should I do if I accidentally overdose on paracetamol?
In case of an overdose, seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms of overdose include nausea, vomiting, sweating, and abdominal pain. Early treatment with an antidote like N-acetylcysteine can prevent severe liver damage.
Interactions and Contraindications
- Can paracetamol be taken with ibuprofen or aspirin?
Yes, paracetamol can be safely taken with ibuprofen or aspirin, as they work differently in the body. However, always consult a healthcare provider before combining medications. - Does paracetamol interact with alcohol?
Yes, combining paracetamol with alcohol increases the risk of liver damage. It is recommended to avoid alcohol while taking paracetamol. - Are there any medications that shouldn’t be taken with paracetamol?
Avoid combining paracetamol with:
- Certain anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine)
- Other drugs containing paracetamol to avoid overdose
- Rifampicin and other liver-metabolized drugs (consult a doctor for specifics)
- Can paracetamol be taken with antibiotics?
Yes, paracetamol is generally safe to take with antibiotics. However, certain combinations may require caution (e.g., isoniazid for tuberculosis). Always consult a doctor for specific advice.
Special Uses
- Is paracetamol effective for headaches and migraines?
Yes, paracetamol is effective for mild to moderate headaches and as an adjunct for migraine relief. It may work best when combined with caffeine or other medications. - Can paracetamol be used to reduce fever?
Yes, paracetamol is widely used to reduce fever in adults and children. It works by acting on the hypothalamus, the brain’s temperature-regulating center. - Does paracetamol work for muscle pain or back pain?
Paracetamol can relieve mild to moderate muscle pain or back pain, but it is less effective for severe or inflammatory pain. - Can paracetamol help with cold and flu symptoms?
Yes, paracetamol is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of cold and flu, such as fever, sore throat, and body aches. Many over-the-counter cold and flu medications contain paracetamol.
Other Concerns
- How long does paracetamol stay in the body?
Paracetamol has a half-life of about 2–3 hours in healthy adults. It is typically eliminated from the body within 24 hours. - What is the difference between paracetamol and ibuprofen?
- Paracetamol: Primarily reduces pain and fever; gentle on the stomach; does not reduce inflammation significantly.
- Ibuprofen: Reduces pain, fever, and inflammation but can irritate the stomach lining.
- Can paracetamol expire? Is it safe to take expired paracetamol?
Paracetamol can expire, and its potency may decrease over time. Using expired paracetamol is not recommended as it may not be effective or could potentially harm you. - How is paracetamol different from aspirin?
- Paracetamol: Pain relief and fever reduction; no significant effect on inflammation or blood clotting.
- Aspirin: Pain relief, fever reduction, reduces inflammation, and acts as a blood thinner.
- Is paracetamol addictive?
No, paracetamol is not addictive. However, misuse or overuse can lead to dependence on pain relief or other health complications.