History of Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely used over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. Its history dates back to the early 19th century when it was first discovered in 1877 by the German chemist Karl Nobecourt. He named it paracetamol after combining para- (meaning “to act against”) with acetylsalicylic
What is PARACETAMOL?
Paracetamol is an analgesic, meaning it is a drug used to relieve mild pain. It is available over-the-counter (OTC) and most commonly used to treat headaches such as tension headache, migraine, and backaches. Paracetamol helps reduce fever, aches, pains, sore throats and toothaches so it can be taken regularly and as soon as you feel any of those signs coming on. While many people opt for prescription medications for their headache symptoms, paracetamol can be the preferred method of treatment for those looking for fast relief without opting for stronger analgesics.
Paracetamol has fewer side effects than other OTC painkillers such as ibuprofen or aspirin which is why it’s often the first choice to soothe minor aches and pains. Side effects can still occur from regular use but they are generally mild such as nausea or vomiting in rare cases. The recommended dosage should not exceed 8 500mg tablets within 24 hours nor should it be taken with alcohol which can increase the risk of liver damage when taken in excess. To ensure optimal safety while taking this medication the user should follow directions on labels and speak to a medical professional
Current Uses of Paracetamol Injection
Paracetamol injection is a quick and effective way to manage pain relief and reduce fever. It can also be used to treat more severe forms of pain such as nerve pain, muscle spasms, migraines, and menstrual cramps. It is especially useful for those who cannot take or tolerate oral medications due to nausea or vomiting.
Paracetamol injection is a fast-acting medication that can help provide pain relief and reduce fever quickly. It also has fewer side effects than other pain medications, so it is safer for those who are sensitive to or intolerant of other medications. Additionally, paracetamol injection can be used to treat more severe forms of pain
Overview of the Article
This article provides an overview of the history of paracetamol and discusses its current uses. Paracetamol was first discovered in 1877 by the German chemist Karl Nobecourt and was named after combining para- with acetylsalicylic. Currently, paracetamol injection is a quick and effective way to manage pain relief and reduce fever . It can also be used to treat more severe forms of pain such as nerve pain, muscle spasms, migraines, and menstrual cramps.
Types of Pain
Severe Pain
Severe pain is intense and usually indicates a serious medical condition or injury. It can be caused by trauma, surgery, cancer, or other illnesses. Severe pain may require the use of prescription medication such as opioids for relief. In some cases, paracetamol injection may also be used to manage severe pain.
Postoperative Pain
Postoperative pain occurs after surgery and can range from mild to severe. Paracetamol injection may be used to effectively manage postoperative pain and reduce the need for opioid medications.
Moderate Pain
Moderate pain is usually less intense than severe pain, but still requires medical attention. Paracetamol injection may be useful for managing moderate pain.
Acute Pain
This is sudden and usually indicates a new injury or illness. Paracetamol injection may be used to help relieve acute pain
Side Effects of Paracetamol Injection
Paracetamol injection is generally safe and well-tolerated, but there may be some side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, itching, swelling, headache, dizziness, and rash. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as liver damage or anaphylaxis can occur. It’s
Administration of Paracetamol Injection
Paracetamol injection is a fast-acting medication and should be administered by a healthcare professional. It is usually given as an intramuscular injection in the upper arm, thigh, or buttocks. Depending on the severity of pain, dosage may vary between 10 to 60 milligrams every 4 to 6 hours. The maximum daily
Oral Administration
Paracetamol can be taken orally either as a tablet, capsule, or suspension. It should be taken with food or milk to reduce the risk of stomach upset. The recommended dose for adults is 325-650 mg every 4-6 hours, up to a maximum of 4 grams per day. For children, the dose varies depending on age and weight and should only be administered under the
Intravenous Administration
Paracetamol injection can be administered intravenously (IV) to provide rapid pain relief and reduce fever. The medication is injected into a vein using a syringe or infusion pump. The dose and frequency of administration will depend on the patient’s condition and response to treatment. It is important to monitor the patient closely during IV administration for any adverse
DOSAGE
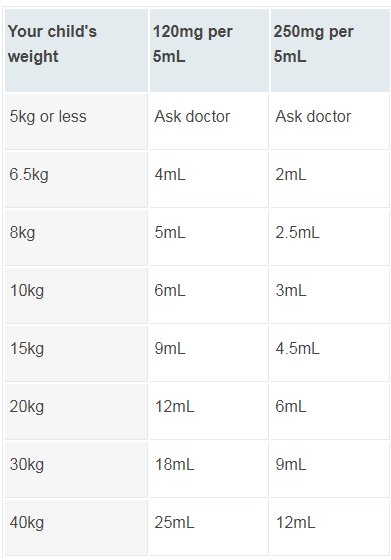
The prescribed dosage of a certain medication varies depending on the patient’s age and weight. For neonates, aged 0-1 month, the recommended dosage is 7.5 mg/kg (0.75 ml/kg) every 6 hours for a maximum amount of 30 mg/kg daily.This should be administered over a period of 15 minutes. For patients aged 1 month or more and weighing 10 kg or less, the recommended dosage is between 10 mg/kg (1 ml/kg) to a maximum of 30 mg/kg, again administered over 15 minutes every 6 hours. For patients that weigh between 10 kg and 50 kg, the recommended dose is 15 mg/kg (1.5 ml/kg), still administered over 15 minutes but with a maximum amount of 60 mg/kg daily. Finally for patients who are 50 kg or above, the suggested dose is 1 g (100 ml) per day administered over 15 minutes with a maximum limit of 4 g daily.
It is important to adhere strictly to these doses as an incorrect dosage may lead to serious health problems or even death in extreme circumstances which would be extremely dangerous from both an individual and societal perspective. Therefore it is strongly encouraged that people educate themselves about dosages and administer
Dosage and Efficacy of Paracetamol Injection
The dosage of paracetamol injection depends on the age, weight, and medical condition of the patient. It is usually given as an intramuscular injection in the upper arm, thigh, or buttocks. For adults, the recommended dose is 10-60 milligrams every 4-6 hours with
Daily Dose for Adults with Normal Renal Function
For adults with normal renal function, the recommended daily dose of paracetamol injection is 4 grams in total, divided into four doses of 10-60 milligrams every 4-6 hours. It is important to not exceed this daily dosage as it can increase the risk of liver damage or other serious side effects. If a larger dose is needed due to severe pain, an opioid analgesic
Daily Dose for Adults with Renal Impairment or Hepatic Impairment
The use of paracetamol injection in adults with renal impairment or hepatic impairment should be done with caution, as there is a risk of increased side effects and toxicity. The maximum daily dosage of paracetamol should not exceed 2 grams for those with mild to moderate renal impairment, and 1 gram for those with severe renal impairment
Analgesic Efficacy in Adults with Severe or Postoperative Pain
Paracetamol injection is an effective analgesic for severe or postoperative pain, as it can provide fast-acting relief. When used as part of a multimodal approach to pain management, paracetamol can help reduce the need for opioid analgesics and their associated side effects . Studies have shown that paracetamol injection can provide similar analgesic efficacy to opioids in adults with moderate to severe pain.
Adverse Reactions and Contraindications of Paracetamol Injection
Although paracetamol injection is generally safe and well-tolerated, there is a risk of adverse reactions and contraindications. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, itching, swelling, headache, dizziness, and rash. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as liver damage, kidney failure, and respiratory depression have been reported. People with liver disease, kidney disease, or alcohol abuse should not take paracetamol injection. In addition, pregnant women should only use paracetamol injection if the potential benefit outweighs the risks.
Storage and Disposal of Paracetamol Injection
Paracetamol injection should be stored at room temperature in its original container, away from heat and direct light. The medication should not be refrigerated or frozen. Keep the medication out of reach of children and pets. It is important to discard any expired or unused paracetamol injection as it may no longer be effective . Expired medication should be disposed of safely, preferably in a hazardous waste container or according to instructions from your local pharmacy.
Who should not take paracetamol?
Paracetamol is a commonly used medication that is used to treat pain and reduce fever. It can be taken in the form of tablets, capsules, syrups or effervescent tablets. However, it is important to note that some people should not take paracetamol. This includes those who have had a previous allergic reaction to paracetamol or any other ingredients found in a paracetamol product they may have taken in the past.
It is also not recommended for people with certain chronic conditions such as kidney disease or liver damage, as paracetamol has been known to cause further damage these organs if taken when they are already weakened by another condition. Additionally, pregnant women should take extra precautions when taking any medications including paracetamol and should always talk to their doctor first before taking them. Lastly, individuals who are already taking other medications may also need to avoid taking medicines containing paracetamol as combining drugs can sometimes have hazardous side effects or negative interactions on the body’s systems. In this case, consulting a doctor prior to taking paracetamol can help prevent any possible health risks from occurring.
What happens if you miss a dose?
If you forget to take a dose of paracetamol, don’t try to “catch up” by taking two doses at once. Doing this can be dangerous and can put you at risk for serious side effects. Instead, if it has been more than four hours since your last dose, just take the missed dose as soon as remembered and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Remember that exceeding the maximum daily recommended dosage of paracetamol is dangerous and should be avoided, even if you have missed a dose.
If you are ever in doubt as to what to do when you miss a paracetamol dose, speak with your doctor or pharmacist for further advice. These professionals will be able to advise on how best to adjust your medication routine so that you are getting the best out of the medicine while minimizing any potential risks associated with usage beyond medical instruction. It’s important to remember that following directions carefully will help ensure your safety and proper use of all medications prescribed or over-the-counter and taking full responsibility for your health through understanding the instructions related to these medicines is key to achieving optimal wellness.
What happens if You overdose?
If someone accidentally takes too much paracetamol, it can cause serious harm to the body. In cases of overdose, it is important to get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center right away in order to prevent further complications. Depending on the amount and time since the overdose, there may be no symptoms during the first 24 hours. However, those who have overdosed may experience pale skin, nausea, sweating, vomiting and loss of appetite. Abdominal pain is also common in these types of situations.
In more severe cases of Paracetamol overdose, long-term liver damage may occur. This should not be taken lightly as it can lead to further health issues and potentially death if not treated swiftly and properly. Those who are suspected of overdosing on Paracetamol should seek medical attention right away so that doctors can properly assess and treat them accordingly. A local hospital or poison control center should be contacted quickly for best results.
Paracetamol Injection Price 💉
In India, the price of Paracetamol injections typically ranges between INR 10 to INR 50 for a single vial or ampule of the generic version. However, it’s important to note that the cost can vary depending on several factors, including the brand, formulation, concentration, packaging size, geographical location, and healthcare setting. Generic versions of Paracetamol injections are generally more affordable than their brand-name counterparts, making them the preferred choice for both healthcare facilities and patients seeking cost-effective pain management and fever reduction solutions. Additionally, government initiatives and public healthcare facilities in India often aim to provide essential medications like Paracetamol injections at subsidized rates or free of charge to ensure accessibility for a wide population. Health insurance coverage may also play a role in reducing out-of-pocket expenses for patients, making this widely used medication accessible and affordable to those in need across the country.
The cost of paracetamol injections can range widely depending on the factors mentioned above. However, to provide a general idea, the price of a single vial or ampule of paracetamol injection in the United States can vary from approximately $2 to $5 for the generic version. Brand-name versions may be more expensive, often exceeding $10 per vial.
It’s important to note that these prices are approximate and subject to change over time. Additionally, healthcare providers and institutions often have access to bulk purchasing agreements or discounts that can significantly reduce the overall cost of medications, including paracetamol injections.
Paracetamol Injection IM or IV Ampoule
Paracetamol injections are available in both intramuscular (IM) and intravenous (IV) forms, provided in ampoules or vials. The choice between IM and IV administration depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, the speed of relief required, and the healthcare provider’s recommendation. Here’s a brief overview of each:
1. Intramuscular (IM) Paracetamol Injection:
Administration: IM injections involve injecting paracetamol directly into a large muscle, typically the thigh or the buttock.
Speed of Action: IM injections generally have a slower onset of action compared to IV administration. It may take some time for the medication to be absorbed into the bloodstream from the muscle.
Use Cases: IM injections are often used when a more prolonged effect is desired, or when IV access is difficult to obtain. They are commonly used in post-operative pain management and for patients who cannot take medications orally.
Dosage: The dosage for IM administration may differ from that of IV administration and should be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
2. Intravenous (IV) Paracetamol Injection:
Administration: IV injections involve directly infusing paracetamol into a vein through a catheter or IV line.
Speed of Action: IV administration provides a faster onset of action as the medication is immediately delivered into the bloodstream, offering quick relief.
Use Cases: IV paracetamol injections are often used in emergency situations when rapid pain relief or fever reduction is required. They are also used in hospital settings for patients who are unable to take medications orally.
Dosage: The dosage for IV administration is typically lower than that for IM administration due to the faster onset of action.
The choice between IM and IV administration should be made by a qualified healthcare provider based on the patient’s specific needs and the medical context. It’s important to note that self-administration of these injections should never be attempted without proper medical guidance, as incorrect administration can lead to complications. Always consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the appropriate route and dosage of Paracetamol injections.
Paracetamol Injection Other Brand Names in India
Crocin IV
Calpol IV
Dolo IV
Pyrigesic IV
Metacin IV
PCM IV
Paracip IV
Paracetamol Injection Time of Action
The time of action of a paracetamol (acetaminophen) injection can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s metabolism, the specific formulation of the injection, and the severity of the condition being treated. However, in general, the onset of action of a paracetamol injection is relatively rapid, usually within 5 to 10 minutes of administration.
The injection allows for the active ingredient (paracetamol) to enter the bloodstream quickly, providing faster relief compared to oral forms of the medication, which may take longer to absorb through the digestive system.
The duration of action can also vary, but the analgesic (pain-relieving) and antipyretic (fever-reducing) effects of a paracetamol injection typically last for about 4 to 6 hours. This means that the relief from pain or reduction in fever may be noticeable for this duration before the effects start to wear off.
It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosing instructions provided by a healthcare professional when using paracetamol injections and to consult with them for specific information about the medication’s action and how it should be administered for your particular medical condition.
Paracetamol Injection Allergy & Contraindications
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered a safe medication when used appropriately, but like any medication, it can have contraindications and the potential for allergic reactions in some individuals. Here are some important considerations:
Contraindications (when you should not use paracetamol injection):
Hypersensitivity or Allergy: If you have a known hypersensitivity or allergy to paracetamol or any of the components of the injection, you should not use it.
Severe Liver Disease: Paracetamol is primarily metabolized by the liver, and it can cause liver damage if used in excessive doses or by individuals with severe liver disease. Therefore, it’s generally contraindicated in people with severe liver impairment.
Warnings and Precautions:
Liver Function: Even in individuals with normal liver function, it’s important not to exceed the recommended dosage of paracetamol, as excessive use can lead to liver damage. People with mild to moderate liver disease should use paracetamol with caution and under medical supervision.
Alcohol Use: Chronic alcohol use can increase the risk of liver damage when taking paracetamol. It’s important to limit or avoid alcohol consumption while using this medication.
Kidney Function: While paracetamol is primarily metabolized by the liver, it can affect the kidneys at high doses or when used over an extended period. People with kidney problems should use paracetamol with caution.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Paracetamol is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding when used at recommended doses. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for guidance, especially in high-risk situations.
Drug Interactions: Paracetamol can interact with other medications. Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking to ensure there are no potential interactions.
Other Health Conditions: Inform your healthcare provider about any other health conditions you may have, such as asthma, as paracetamol may be a safer choice than certain other pain relievers for individuals with specific medical conditions.
Allergic Reactions:
Allergic reactions to paracetamol are relatively rare but can occur. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
Rash or hives
Itching
Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
Difficulty breathing
Severe dizziness or lightheadedness
If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction after receiving a paracetamol injection, seek immediate medical attention.
It’s crucial to use paracetamol injections under the guidance and prescription of a healthcare provider, and if you have any concerns about allergies or contraindications, discuss them with your healthcare professional. They can provide you with personalized advice and treatment options.
Paracetamol Injection BP Monograph
A British Pharmacopoeia (BP) monograph provides detailed information about a specific medication, including its composition, quality standards, manufacturing process, and guidelines for its use. Below, I’ve outlined a simplified BP monograph for Paracetamol Injection, adhering to general pharmaceutical standards. Please note that the specific details may vary depending on the manufacturer and version of the monograph.
Paracetamol Injection BP Monograph
1. Name of the Medicinal Product:
Paracetamol Injection BP
2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition:
Each milliliter of the injection contains [Specify the quantity] of paracetamol as the active ingredient.
3. Pharmaceutical Form:
Clear, colorless solution for injection.
4. Clinical Particulars:
4.1 Therapeutic Indications:
Paracetamol injection is indicated for the relief of mild to moderate pain and the reduction of fever.
4.2 Posology and Method of Administration:
The dosage and administration should be determined by a healthcare professional.
The injection is typically administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM).
Dosage and administration guidelines will vary based on the patient’s age, weight, and medical condition.
4.3 Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity or allergy to paracetamol or any components of the injection.
Severe liver disease.
4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use:
Use with caution in patients with liver or kidney impairment.
Avoid alcohol consumption during treatment.
Special precautions may be needed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
4.5 Interactions with Other Medicaments and Other Forms of Interaction:
Paracetamol may interact with certain medications, including those affecting liver enzymes. Consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive list of potential interactions.
4.6 Pregnancy and Lactation:
Paracetamol is generally considered safe during pregnancy and lactation when used as directed. However, consult a healthcare provider for specific guidance.
4.7 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines:
No known effects on the ability to drive or use machinery.
4.8 Undesirable Effects:
Common side effects
Rare but serious side effects
4.9 Overdose:
Symptoms of overdose may include
Nausea and vomiting
Loss of appetite
Excessive sweating
Extreme tiredness or weakness
Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right side
Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
Confusion or altered mental state
Unconsciousness or coma.
Treatment of overdose typically involves supportive care and may include antidotal therapy.
5. Pharmaceutical Particulars:
5.1 List of Excipients:
Water for Injection: Often used as the solvent or diluent for the injection.
Sodium Hydroxide: Used for pH adjustment.
Hydrochloric Acid: Used for pH adjustment.
Sodium Metabisulfite: A preservative.
Mannitol: A sugar alcohol used as a stabilizer or tonicity-adjusting agent.
Disodium Edetate (EDTA): Used as a stabilizing or chelating agent.
Propylene Glycol: Occasionally used as a solvent or co-solvent.
Polysorbate 80: An emulsifying agent.
5.2 Incompatibilities:
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) injections can have known incompatibilities when mixed with other medications or solutions. These incompatibilities can lead to chemical reactions or physical changes that may affect the stability and safety of the injection. Here are some known incompatibilities with paracetamol injections:
Incompatibility with Other Drugs: Paracetamol injections should not be mixed in the same syringe or IV line with other drugs unless compatibility is confirmed by a healthcare professional or pharmacist. Mixing paracetamol with other medications can lead to precipitation or chemical reactions that may render the drugs ineffective or harmful.
Incompatibility with Certain Solutions: Paracetamol injections should be administered with compatible intravenous solutions as specified by the manufacturer’s instructions. Mixing paracetamol with incompatible solutions can result in precipitation or changes in the solution’s pH, potentially leading to reduced efficacy or adverse effects.
Incompatibility with Certain Containers: Some containers or materials used in the administration of paracetamol injections may not be compatible with the formulation. It’s important to use appropriate materials and equipment as recommended by healthcare professionals.
Incompatibility with Certain Intravenous Lines: Paracetamol injections should be administered using dedicated IV lines to avoid potential interactions with other medications or fluids in the same line.
It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions, as well as the guidance of healthcare professionals, when administering paracetamol injections to ensure compatibility and prevent potential adverse effects. Healthcare providers and pharmacists can provide specific recommendations based on the formulation and the patient’s medical condition.
5.3 Shelf Life:
The shelf life of the product should be mentioned here.
5.4 Special Precautions for Storage:
Store at [temperature range] in the original packaging.
6. Legal Category:
This section indicates the legal classification of the medicine.
7. Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Name and address of the company holding the marketing authorization.
8. Marketing Authorisation Number(s):
Mention the authorization number(s) if applicable.
9. Date of First Authorisation/Renewal of the Authorisation:
Provide the date of initial authorization or renewal.
10. Date of Revision of the Text:
Specify the date when the monograph was last revised.
Please note that this is a simplified template, and a comprehensive BP monograph for Paracetamol Injection would contain additional detailed information and specifications. Always consult the latest official British Pharmacopoeia for the most up-to-date and complete monograph for any medication.
Conclusion
Paracetamol injection is an effective and safe medication for managing postoperative pain, acute pain, and moderate pain. It has a fast-acting effect that can provide relief in minutes. However, it should be administered cautiously in patients with renal impairment or hepatic impairment to reduce the risk of side effects and toxicity.