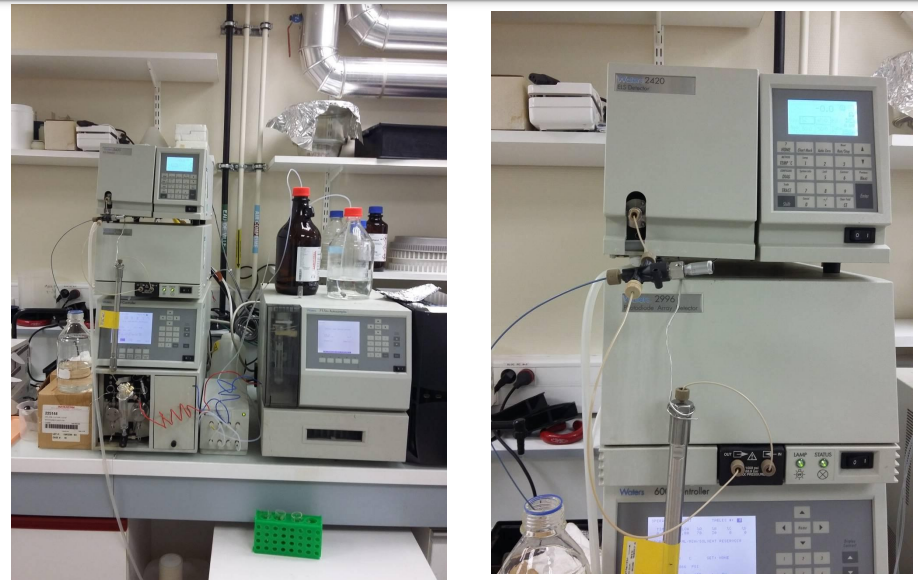
If you want to know completely about High-Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLC you are at the right place.In this article you can find from the basics of chromatography along with the Principle of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and parameters that are used as a standard for a particular compound in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC).Types of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Instrumentation and applications uses of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)are provided here. You can download the PPT AND PDF on HPLC in the following paragraphs.
What is chromatography ?
Chromatography is a separation technique that uses the size, shape, chemical properties or charge of molecules in a sample to separate the sample into its constituent components.
Chromatography is a physical method of separation in which the components to be separated are, distributed two phases, one of which is stationary phase while the other is mobile phase, moves in a definite direction.
Chromatography Principle
Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in mixture applied onto the surface or into the solid, and fluid stationary phase (stable phase) is separating from each other while moving with the aid of a mobile phase. e factors effective on this separation process include molecular characteristics related to adsorption (liquid-solid), partition (liquid-solid), and affinity or differences among their molecular weights. Because of these differences, some components of the mixture stay longer in the stationary phase, and they move slowly in the chromatography system, while others pass rapidly into mobile phase, and leave the system faster
Why HPLC?
- HPLC came about because not all compounds can be vaporized and analyzed on a GC
- Separation of a wider range of compounds — high MW, polar, and ionic compounds
- Highly efficient separations achieved in HPLC due to interactions of both m.p. and s.p. with the components of a mixture.
- Improved separation within a much shorter time
What is High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)?
HPLC represents an automated system for the separation of compounds in mixture using a liquid mobile phase, which is passed across the stationary phase under high pressure in order to speed up the operation.
The effluent of the column is monitored by special detectors and the signals for the eluted components are recorded in a special recorder which amplifies such signals and record them as peaks similar to those obtained in gas chromatography.
HPLC PRINCIPLE
HPLC works on the principle of Affinity chromatography. The solution of the sample is injected into a column of a porous material (stationary phase) and a liquid (mobile phase) is pumped at high pressure through the column. The mixture on travelling through the stationary phase splits into its constituents and the component with high affinity for stationary phase travels late whereas one with less affinity elutes fast. This is also based partition coefficient of the material.
To make you understand, in simple terms HPLC follows the principle of separation in both normal phase mode and reverse phase mode is adsorption. When a mixture of components are introduced into a HPLC column, they travel according to their relative affinities towards the stationary phase. The component which has more affinity towards the adsorbent, travels slower. The component which has less affinity towards the stationary phase travels faster. Since no 2 components have the same affinity towards the stationary phase, the components are separated.

TYPES OF HPLC TECHNIQUES:
A. Based on modes of chromatography
1. Normal phase mode
2.Reverse phase mode
B. Based on principle of separation
1. Adsorption chromatography
2. Ion exchange chromatography
3. Ion pair chromatography
4.Size exclusion(or)Gel permeation chromatography
5. Affinity chromatography
6. Chiral phase chromatography
C. Based on elution technique
1. Isocratic separation
2. Gradient separation
D. Based on the scale of operation
1. Analytical HPLC
2. Preparative HPLC
E. Based on the type of analysis
1. Qualitative analysis
2. Quantitative analysis
HPLC INSTRUMENTATON BASIC INFORMATION:
1. Solvent delivery system
2. Pumps
3. Sample injection system
4. Column
5. Detectors
6. Recorders and Integrators
Applications of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Pharmaceutical applications of HPLC are Tablet dissolution study of pharmaceutical dosages form, Shelf-life determinations of pharmaceutical products, Identification of active ingredients of dosage forms, Pharmaceutical quality control applications, Detection of phenolic compounds in Drinking Water, Identification of compounds in sediment samples, Bio-monitoring of pollutant, Quantification of the drug in biological samples. • Identification of anabolic steroids in serum, urine, sweat, and hair,Determination of cocaine and metabolites in blood Clinical Quantification of ions in human urine Analysis of antibiotics in blood plasma, Estimation of bilirubin and biliverdin in blood plasma in case of hepatic disorders,Detection of endogenous neuropeptides in extracellular fluids of brain.
- Other applications include testing the quality of soft drink and drinking water, Analysis of beer, Sugar analysis in fruit juices, Analysis of polycyclic compounds in vegetables,Trace analysis of military high explosives in agricultural crops.
- Chemical Separations
- Purification
.
HPLC USES
1. Separations fast and efficient (high resolution power)
2. Continuous monitoring of the column effluent
3. It can be applied to the separation and analysis of very complex mixtures
4. Accurate quantitative measurements.
5. Repetitive and reproducible analysis using the same column.
6. Adsorption, partition, ion exchange and exclusion column separations are excellently made
7. HPLC is more versatile than GLC in some respects, because it has the advantage of not being restricted to volatile and thermally stable solute and the choice of mobile and stationary phases is much wider in HPLC
8. Both aqueous and non aqueous samples can be analyzed with little or no sample pretreatment
9. A variety of solvents and column packings are available, providing a high degree of selectivity for specific analyses.
10. It provides a means for determination of multiple components in a single analysis.
Advantages of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- By using this High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) technique it is possible to perform structural, and functional analysis, and purification of many molecules within a short time.
- This technique yields perfect results in the separation, and identification of amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, steroids, and other biologically active molecules
- In HPLC, mobile phase passes throuıgh columns under 10–400 atmospheric pressure, and with a high (0.1–5 cm//sec) flow rate.
- In this technique, use of small particles,and application of high pressure on the rate of solvent flow increases separation power, of HPLC and the analysis is completed within a short time
PARAMETERS USED IN HPLC:
1.Retention time
2.Retention volume
3.Separation factor
4. Resolution
5. Height Equivalent to a Theoretical Plate (HETP)
6. Efficiency
7. Asymmetry factor
What are hplc detectors
The work of detector is to detect and give the information to the recorder which shows it in a form of a chromatogram. Every compounds has its own properties which is not completely the same with one another, thus this arises a need to have different detectors for different compounds. Before beginning the separation by HPLC it is thus very important to study about the nature of the compound and select the detector accordingly. The selection of wrong detector misguides our journey of separation and quantification.
Types of hplc detectors
1. Refractive index detectors
2. U.V detectors
3. Fluorescence detectors
4. Electro chemical detectors
5. Evaporative light scattering detectors
6. IR detectors
7. Photo diode array detector:
what are most common hplc detector
Detectors used depends upon the property of the compounds to be separated. Detectors are elemental detectors (atomic absorption/emission, inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry and microwave-induced plasma); optical detectors (UV/visible, IR/Raman, optical activity, evaporative light scattering and refractive index); luminescent detectors (fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemiluminescence/bioluminescence); electrochemical detectors (potentiometry, novel material/modified electrodes, array electrodes and pulsed
and oscillometric techniques); mass spectrometric detectors (time-of-flight/MALDI, Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, electrospray/thermospray, atmospheric pressure ionization and particle beam); and other detection systems (nuclear magnetic resonance, radioactivity detectors, surface plasmon resonance)
MODES OF HPLC
HPLC Modes
• Normal-phase (NPC)
– Separation based on adsorption of the analyte onto a polar surface (silica)
• Reversed-phase (RPC)
– Separation based on analytes’ partition coefficients between the mobile phase and the bonded stationary phase
• Ion-exchange (IEC)
– Separation based on ion-exchanging with the counter-ions and ionic interaction with the bonded ionic group
• Size-exclusion (SEC orGFC)
– Separation based on analyte’s molecular size and sieving action of the column packing
Limitations of HPLC
- Lack of a Universal Detector. The lack of a universal detector is often mentioned, although the UV–vis detector comes close to one for chromophoric compounds. Refractive index detection fits the bill, but suffers from low sensitivity and incompatibility with gradient elution. Evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD) was a contender, but was surpassed by charged aerosol detection (CAD). CAD uses a nebulizer with corona discharge detection and has better sensitivity (low ng) and ease-of-use than ELSD
- Less Separation Efficiency than Capillary Gas Chromatography Conventional. HPLC has a practi-cal peak capacity (Pc) of ~200 using columns with ~20,000 plates under gradient conditions — not particularly effective for very complex samples
- Relatively More Difficult for Novices The bewildering number of HPLC modules, columns, mobile phases, and operating parameters renders HPLC difficult for the novice.
- Still Arduous, Particularly for Regulated Testing HPLC is versatile, quantitative, sensi-tive, and extremely precise. It can also be time-consuming and arduous, particularly for regulated analysis under good manufacturing practices (GMP).
Conclusion
HPLC is a complex technique because of its myriad combinations of modules, columns or mobile phases, and operating parameters. Initially chromatographic techniques were used to separate substances based on their color as was the case with herbal pigments. With time its application area was extended considerably. Nowadays, chromatography is accepted as an extremely sensitive, and effective separation method.
HPLC technique which has many superior features including especially its higher sensitivity, rapid turnover rate, its use as a quantitative method, can purify amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, drugs, antibiotics, and steroids
References
- Handbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis by HPLC, S. A huja and M.W. Dong , Ed s. (Elsevier/Academic Press, 2005).
- HPLC for Pharma ceutical Scientists, Y.V. Kazakevich and R. LoBrutto, Eds. (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2007).
- C.F. Poole, Essence of Chromatography (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002).
- Chromatog raphy: A Scien ce of Discovery, R.L. Wixom and C.L . Gehrke, Eds. (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2010).
- UHPLC in Life Scie nce s, D. Guillarme, J-L Veuthey, and R.M. Smith, Eds. (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2012).
- M. Swartz, M. Emmanuel, A. Awad, and D. Hartley, “Advances in HPLC Systems Technology” supplement to LCGC North Am. 27(4), 40–48 (2009).
- Mass Spectrometry for Drug Discovery and Drug Development, W.A. Korfmacher, Ed.(Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2013).
- J.E. MacNair, K.C. Lewis, and J.W. Jorgenson, Anal. Chem. 69, 983–989 (1997).
- M.W. Dong, LCGC North Am. 25(7), 656– 666 (2007).
- N. Wu a nd A.M. Clausen, J. Sep. Sci. 30,1167–1182 (2007).
- D. Gui ll arme and M.W. Dong , Amer. Pharm. Rev., (2013) submitted.
- M.W. Dong , D. Guillarme, S. Fekete, R. Rangelova, J. Richa rds, D. Prudhomme, and N.P. Chetwyn, J. Chromatogr. A. submitted.
- L. Sannes, “Commercia lizing Biomarkers in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Application– Overview,” Insight Pharma Report
Important Questions on HPLC
Questions
1. Contrast the advantages and disadvantages of thin layer chromatography
(TLC) versus modern HPLC.
2. What does HPLC stand for?
3. What are the advantages of dual reciprocating pumps have over syringe
pumps?
4. How much does a basic HPLC system cost?
5. What are the sub-categories of liquid chromatography?
6. What is the difference between normal phase HPLC and reverse phase
HPLC? Which is most commonly used today?
7. What chemical factors determine if a chemical will be analyzed in a GC or LC?
8. Can moderately volatile, thermally stable chemical be analyzed on an LC?
9. Why do we filter analyte solutions before injection into an HPLC?
10. Draw a basic HPLC system and label all of the components.
11. Why are pressurized gases used in HPLC?
12. What two preparatory steps must be taken before a solvent can be used as an HPLC mobile phase?
In general, what is the maximum pressure limit of standard HPLC systems?
13. What is the purpose of the proportioning valve? How does this reduce the cost of an HPLC?
14. What is the difference in isocratic and gradient programming? Why is gradient programming sometimes necessary?
15. Why are dual piston pumps preferred over single piston pumps?
16. What is the purpose of a pulse damper?
17. Why are six-port valves used for injecting samples in HPLC?
18. Draw and explain how a six-port valve works.
19. Why are in-line filters used in HPLC systems?
20. What is the composition of the stationary phase and purpose of the guard
column?
21. What are common stationary phases used in reverse phase HPLC?
22. Why do chromatographers purchase their analytical columns instead of self packing their own?
23. How will a poorly packed column affect performance?
24. What is the relationship between performance (resolution) and stationary
phase particle size?
25. Compile a list of HPLC detectors and provide a list of chemicals each can be
used to analyze.
26. Name three advanced types of LC.
27. Why is U-HPLC superior to standard HPLC?
28. How does IC differ from standard HPLC?
29. What is the purpose of the suppressor column in IC?
30. Draw a suppressor column for cation analysis in IC. Explain how it works.
Hope you like the article. please leave a comment if you have any doubts.