Contents of the powerpoint on Plasma membrane – physiology structure and role in drug absorption include:
Content
Introduction
Physiology of Plasma membrane.
Structure,
composition,
functions.
Transport across cell membrane.
Conclusion
References
Plasma membrane structure
Definition:
The Plasma membrane is a thin bi- layered structure which surrounds each cell, consists of lipids (phospholipids 75%, cholesterol 20%,glycolipids 5%), proteins (partially or completely embedded), carbohydrates etc.,
~6-10 nm thick.
Plasma membrane is asymmetrical
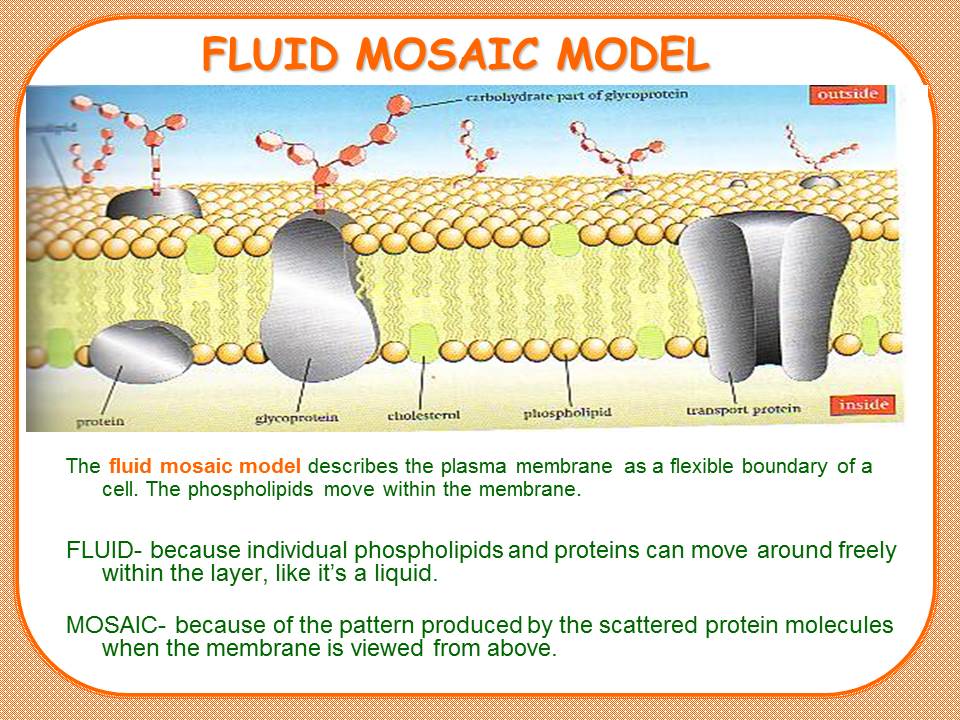
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as a flexible boundary of a cell. The phospholipids move within the membrane.
FLUID- because individual phospholipids and proteins can move around freely within the layer, like it’s a liquid.
MOSAIC- because of the pattern produced by the scattered protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from above.
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are lipids with a phosphate attached to them.
The phospholipids are very flexible and behave similar to a fluid.
The lipids in the plasma membrane can be saturated or unsaturated, the more saturated lipids in a membrane the more rigid the plasma membrane is. The more unsaturated lipids, the more flexible the membrane is.
The phospholipids have a water soluble head, and water insoluble lipid tails.
Other lipids in plasma membrane
GLYCOLIPIDS: Phospholipid molecule attached with a carbohydrate chain straight or branched to its hydrophilic head.
CHOLESTEROL: lipid found in animal plasma membranes which reduces the permeability to most biological molecules.
it regulates membrane fluidity over the range of physiological temperatures.
cholesterol also functions in intracellular transport, cell signaling and nerve conduction.
cholesterol has also been implicated in cell signaling processes, assisting in the formation of lipid rafts in the plasma membrane.
In many neurons a myelin sheath, rich in cholesterol since it is derived from compacted layers of Schwann cell membrane, provides insulation for more efficient conduction of impulses.
Cholesterol present between the fatty acids chains, binds with OH side to the phosphate of lipid by H-bonding.
Download the powerpoint by liking us on Facebook
[like-gate][/like-gate]
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3546″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PPT here[/button]
You can also download the PDF onPlasma membrane – physiology structure and role in drug absorption by clicking here
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3529″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PDF here[/button]
 Unlike the actual test which only Final year Bpharm students can take, this free mock GPAT test can be taken by anyone right from B.Pharm 1st year to M.pharm students. This will give an idea about GPAT to all those who want to write GPAT in future also.
Unlike the actual test which only Final year Bpharm students can take, this free mock GPAT test can be taken by anyone right from B.Pharm 1st year to M.pharm students. This will give an idea about GPAT to all those who want to write GPAT in future also.