Contents of the powerpoint on Lymphatic transport of drugs include:
CONTENTS
Introduction
Physiology of lymphatic system
Intestinal lymphatic drug transport
Promotion of intestinal lymphatic drug transport
Prodrug approaches for enhanced lymphatic delivery
Formulation approaches for enhanced intestinal lymphatic transport
Conclusion
References
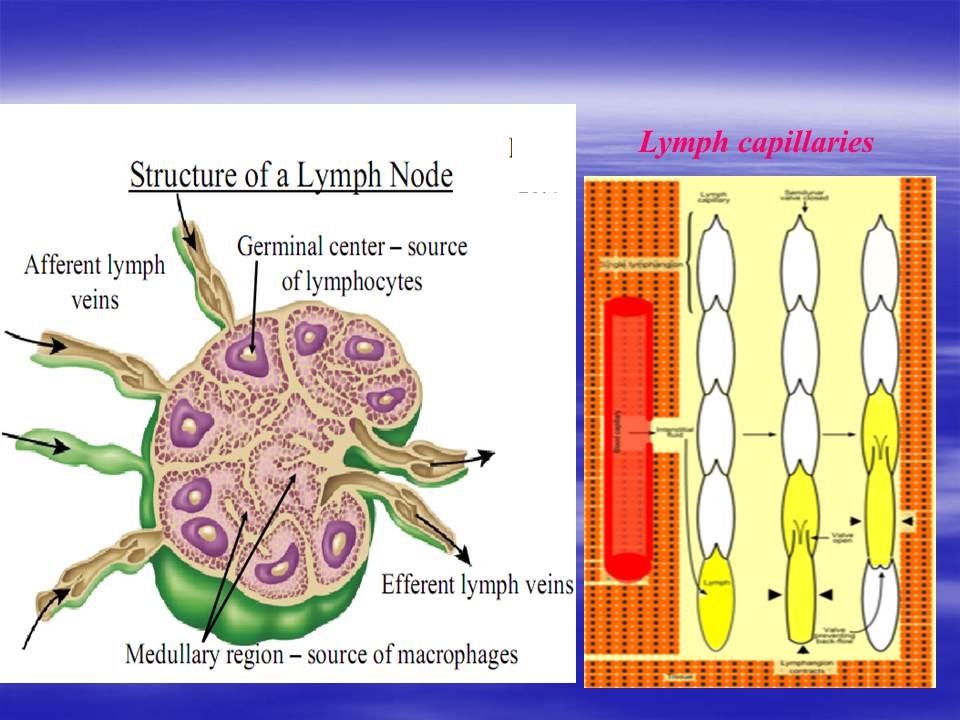
Lymphatic system
Lymphatic system is closed system of lymph channels through which lymph flows.
Lymphatic system is one way system and allows the lymph tissue spaces to the blood
The lymphatic system can be broadly divided into the conducting system and the lymphoid tissue.
The conducting system carries the lymph and consists of tubular vessels that include the lymph capillaries, the lymph vessels, and the right and thoracic ducts.
Lymphatic conducting system
Tubular vessels transport back lymph to the blood ultimately replacing the volume lost from the blood during the formation of the interstitial fluid. These channels are the lymphatic channels or simply called lymphatics.
lymphatic conducting system broadly consists of two types of channels—the initial lymphatics or lymph capillaries that specialize in collection of the lymph from the ISF, and the larger lymph vessels that propel the lymph forward
Lymphoid tissue
Lymphoid tissue is concerned with immune functions in defending the body against the infections and spread of tumors. It consists of connective tissue with various types of white blood cells lymphocytes
The lymphoid tissue may be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending upon the stage of lymphocyte development and maturation.
Download the powerpoint by liking us on Facebook
[like-gate][/like-gate]
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3544″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PPT here[/button]
You can also download the PDF onLymphatic transport of drugs by clicking here
[button url=”http://pharmawiki.in/?attachment_id=3527″ style=”glass” background=”#1782f9″ color=”#ffffff” size=”4″ center=”yes” icon=”icon: download”]Download PDF here[/button]