Hot Air Oven Working Principle Sterilization Labelled Diagram Temperature [ #PDF PPT ] is the main theme of this article. Sterilization and aseptic processing are essential practices for healthcare product manufacture and many healthcare services. The execution of these processes in an appropriate manner is essential for patient safety.
A hot air oven is used to sterilize equipment and materials used in the medical field. A hot air oven is a type of dry heat sterilization. Dry heat sterilization is used on equipment that cannot be wet, and on material that will not melt, catch fire, or change form when exposed to high temperatures. Moist heat sterilization uses water to boil items or steam them to sterilize and does not take as long as dry heat sterilization. Examples of items that are not sterilized in a hot air oven are surgical dressings, rubber items, or plastic material. Items that are sterilized in a hot air oven include:
Glassware (petri dishes, flasks, pipettes, and test tubes)
Powders (starch, zinc oxide, and sulfadiazine)
Materials that contain oils
Metal equipment (scalpels, scissors, and blades)
Glass test tubes can be sterilized using a hot air oven
Glass test tubes can be sterilized using a hot air oven
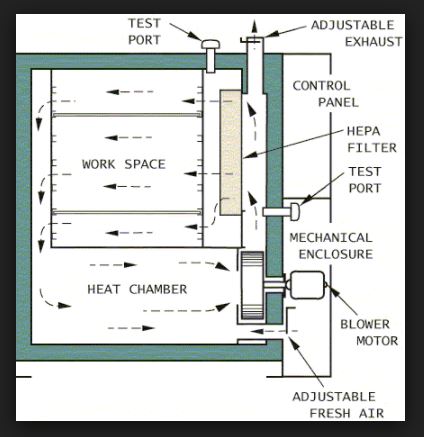
Hot air ovens use extremely high temperatures over several hours to destroy microorganisms and bacterial spores. The ovens use conduction to sterilize items by heating the outside surfaces of the item, which then absorbs the heat and moves it towards the center of the item.
The commonly-used temperatures and time that hot air ovens need to sterilize materials is 170 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, 160 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes, and 150 degrees Celsius for 150 minutes.

Principle of HOT AIR OVEN (Dry heat sterilization)
Sterilizing by dry heat is accomplished by conduction. The heat is absorbed by the outside surface of the item, then passes towards the centre of the item, layer by layer. The entire item will eventually reach the temperature required for sterilization to take place.
Dry heat does most of the damage by oxidizing molecules. The essential cell constituents are destroyed and the organism dies. The temperature is maintained for almost an hour to kill the most difficult of the resistant spores.
The most common time-temperature relationships for sterilization with hot air sterilizers are
170°C (340°F) for 30 minutes,
160°C (320°F) for 60 minutes, and
150°C (300°F) for 150 minutes or longer depending up the volume.
Note: Bacillus atrophaeus spores should be used to monitor the sterilization process for dry heat because they are more resistant to dry heat than the spores of Geobacillus stearothermophilus. The primary lethal process is considered to be oxidation of cell constituents.

Types of HOT AIR OVEN
the static-air type and
the forced-air type.
There are two types of dry-heat sterilizers:
the static-air type and
the forced-air type.
The static-air type is referred to as the oven-type sterilizer as heating coils in the bottom of the unit cause the hot air to rise inside the chamber via gravity convection. This type of dry-heat sterilizer is much slower in heating, requires longer time to reach sterilizing temperature, and is less uniform in temperature control throughout the chamber than is the forced-air type.
The forced-air or mechanical convection sterilizer is equipped with a motor-driven blower that circulates heated air throughout the chamber at a high velocity, permitting a more rapid transfer of energy from the air to the instruments.
Hot Air Oven Labelled Diagram
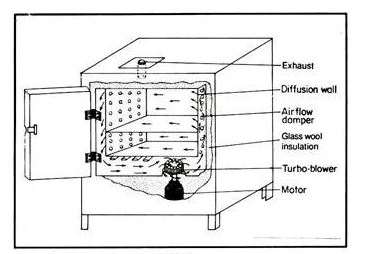
Uses of HOT AIR OVEN (dry heat sterilization)
A dry heat cabinet is easy to install and has relatively low operating costs;
It penetrates materials
It is nontoxic and does not harm the environment;
And it is noncorrosive for metal and sharp instruments.
Disadvantages for dry heat sterilization
Time consuming method because of slow rate of heat penetration and microbial killing.
High temperatures are not suitable for most materials.
Working Principle of HOT AIR OVEN
Sterilizing by dry heat is accomplished by conduction. The heat is absorbed by the outside surface of the item, then passes towards the centre of the item, layer by layer. The entire item will eventually reach the temperature required for sterilization to take place.
Dry heat does most of the damage by oxidizing molecules. The essential cell constituents are destroyed and the organism dies. The temperature is maintained for almost an hour to kill the most difficult of the resistant spores.
The most common time-temperature relationships for sterilization with hot air sterilizers are
170°C (340°F) for 30 minutes,
160°C (320°F) for 60 minutes, and
150°C (300°F) for 150 minutes or longer depending up the volume.
Different Types of Hot Air Ovens
There are two types of hot air ovens. One is a forced air hot air oven and the other is a static air hot air oven. The forced air hot air oven is more effective than the static air hot air oven.
The forced air hot air oven works by heating the oven and using a fan to move the hot air around. This helps prevent the hot air from rising to the top of the oven and keeping the cooler air at the bottom. The fan keeps the hot air moving around at a consistent temperature throughout the oven.
The static air hot air oven works by using a heating coil at the bottom of the oven. The heat rises throughout the oven and takes a longer time to reach the desired temperature. Since the heat is not circulated as with a forced air hot air oven the temperature is not consistent throughout the oven.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE of HOT AIR OVEN
Aim:
To lay down the procedure for operation of Hot Air Oven.
Procedure:
1. Connect the power supply.
2. Switch “ON” the main power supply and instrument mains.
Temperature setting
3. Press SET POINT (x/w) key to set the required temperature. press ↑ to
increase the temperature and ↓ to reduce the temperature
4. The temp. Sensor will maintain the set temp which is indicated by the blinking
of set temp on the display screen.
5. The duration of time can also be adjusted using the time adjustment knob
6. After use,SWITCH OFF the power supply.
Safety & Precautions:
=> Maximum Temp. : 350o
C.
=> Ensure that the Exhaust blower is ON before starting the oven.
=> Ensure the GN2 plant is UP.
=> Ensure that temperature does not shoot higher than the set temperature
Cleaning:
# Wipe the surface, walls, top, bottom and trays of the oven with dry lint free
cloth on daily basis so that there will be no dust particles in the oven.
# Wipe all the parts and outer surface of the Oven with wet lint free cloth
soaked in purified water, on weekly basis and fill the weekly cleaning
Note: Bacillus atrophaeus spores should be used to monitor the sterilization process for dry heat because they are more resistant to dry heat than the spores of Geobacillus stearothermophilus. The primary lethal process is considered to be oxidation of cell constituents.
Hot Air Oven Uses ( Advantages) :
Items that are sterilized in a hot air oven include:
Glassware (petri dishes, flasks, pipettes, and test tubes)
Powders (starch, zinc oxide, and sulfadiazine)
Materials that contain oils
Metal equipment (scalpels, scissors, and blades)
Glass test tubes can be sterilized using a hot air oven
Glass test tubes can be sterilized using a hot air oven
Hot air ovens use extremely high temperatures over several hours to destroy microorganisms and bacterial spores. The ovens use conduction to sterilize items by heating the outside surfaces of the item, which then absorbs the heat and moves it towards the center of the item.
Note:Items that are not sterilized in a hot air oven are surgical dressings, rubber items, or plastic material.
Disadvantages for dry heat sterilization
Time consuming method because of slow rate of heat penetration and microbial killing.
High temperatures are not suitable for most materials.
Incoming Searches:
hot air oven , hotair oven, air oven principle, principle of hot air oven, hot air oven drawing , hot air oven sterilization , hot air oven uses , labelled diagram of hot air oven , hot air oven diagram , working principle of hot air oven pdf , hot air oven principle pdf, hot air oven temperature , uses of hot air oven , hot air oven temperature , hot air oven working , air oven, hot air oven working principle , hot air oven principle , hot air oven principle , hot air oven temperature and time , hotair oven , principle of hot air oven , principle of hot air oven, hot air oven pdf , hotair oven , hot air oven uses , working principle of hot air oven pdf , hot air oven working , hot air oven principle pdf, hot air oven principle pdf , hot air oven working principle , hot air oven principle pdf , uses of hot air oven , hot air oven images , hot air oven working , hot air oven working , hot air oven working principle , hot air oven working principle , laboratory hot air oven , calibration of hot air oven , validation of hot air oven pdf , hot air oven pdf , laboratory hot air oven diagram , oven working principle, hot air sterilization [#PDF PPT] Hot Air Oven Working Principle Sterilization Diagram SOP Uses Temperature