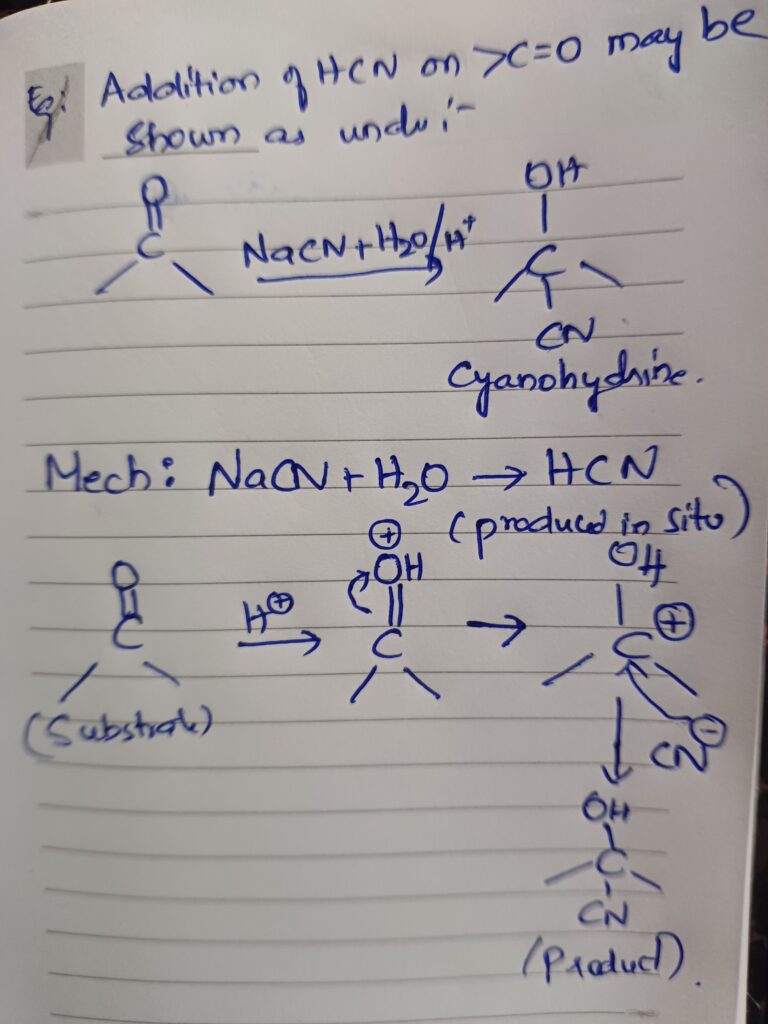
This article presents an overview of uses of Paracetamol as a widely used medication. Most common types of ailments for which Paracetamol is used are fever, headaches, muscle aches, toothaches etc. Paracetamol is chemically known as acetaminophen, is a widely used medication known for its pain-relieving and fever-reducing properties. It is available over-the-counter and is recognized as a safe and effective option for managing various types of pain and discomfort by doctors and scientists.
Primary uses of Paracetamol:
Fever Reduction
Pain Relief
Do you know how paracetamol acts in Pain Relief? Mechanism of action of Paracetamol in relieving pain and the Dosage and administration guidelines for pain relief are given in this article. Know How Paracetamol helps in reducing fever along with Conditions or illnesses that often involve fever and the use of Paracetamol (e.g., common cold, flu).
Other things like Paracetamol as a solution for alleviating menstrual pain, Role of Paracetamol in reducing menstrual cramps. Potential side effects or adverse reactions of Paracetamol in addition to Important precautions to take before using Paracetamol (e.g., liver or kidney conditions, interaction with other medications) are mentioned below.
I. Introduction
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely used medication known for its pain-relieving and fever-reducing properties. It is available over-the-counter and is recognized as a safe and effective option for managing various types of pain and discomfort.
A. Mechanism of Action: Paracetamol works by inhibiting the production of certain chemicals in the body that contribute to pain and inflammation, primarily in the central nervous system.
II. Pain Relief
B. Common Types of Pain: Paracetamol is commonly used to alleviate different types of pain, including headaches, muscle aches, toothaches, and joint pain. It is effective for mild to moderate pain.
C. Dosage and Administration: Proper dosing guidelines should be followed based on the individual’s age, weight, and the severity of the pain. It is important to read and follow the instructions provided on the packaging or consult a healthcare professional for guidance. MORE DOSAGE DETAILS OF PARACETAMOL CLICK HERE
III. Fever Reduction
A. How Paracetamol Helps: Paracetamol is effective in reducing fever by acting on the hypothalamus in the brain, which regulates body temperature. It helps to bring down elevated body temperature.
B. Conditions Involving Fever: Paracetamol is commonly used to manage fever associated with various conditions such as the common cold, flu, and other infections.
C. Proper Dosing Considerations: The dosage of Paracetamol for fever reduction is based on the individual’s age and weight. It is important to follow the recommended dosing intervals and not exceed the maximum daily dose.
Click here for exact dosage details of Paracetamol
IV. Cold and Flu Symptoms
A. Relief of Symptoms: Paracetamol provides relief from common symptoms associated with cold and flu, including headache, sore throat, body aches, and fever. It helps improve overall comfort during the illness.
B. Common Symptoms Addressed: Paracetamol is particularly effective in reducing headache pain and alleviating body aches and sore throat, making it a suitable choice for managing these symptoms.
C. Usage Recommendations: It is advisable to take Paracetamol as directed on the packaging or as recommended by a healthcare professional. It is important to consider other medications being taken and any specific instructions or warnings provided.
V. Menstrual Pain
A. Alleviating Menstrual Pain: Paracetamol is commonly used to relieve menstrual pain and discomfort, including menstrual cramps. It helps reduce the intensity of cramps and provides relief.
B. Role in Reducing Menstrual Cramps: Paracetamol works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for triggering uterine contractions and causing menstrual cramps.
C. Proper Use and Dosing Guidelines: It is recommended to take Paracetamol at the onset of menstrual pain and follow the recommended dosage instructions. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice, especially for severe or persistent menstrual pain.
VI. Precautions and Considerations
A. Potential Side Effects: Paracetamol is generally safe when used as directed, but it may have side effects in rare cases. These can include allergic reactions or liver damage if taken in excessive doses or with alcohol.
B. Precautions for Specific Conditions: Individuals with liver or kidney conditions, as well as those taking other medications, should exercise caution when using Paracetamol. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and appropriate.
C. Consulting a Healthcare Professional: If there are any concerns or questions regarding the use of Paracetamol, it is recommended to seek advice from a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Paracetamol uses in Fever
Acetaminophen is used medication for reducing fever and relieving mild to moderate pain. Here are some ways paracetamol is used in the context of fever:
Fever reduction: Paracetamol is widely used to lower fever in both adults and children. It works by acting on the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates body temperature, and helps to bring down elevated body temperature.
Pain relief: Paracetamol can also help alleviate pain associated with fever, such as headaches, muscle aches, and sore throat. It is particularly effective in managing mild to moderate pain.
Symptom relief: In addition to reducing fever and relieving pain, paracetamol can also provide symptomatic relief for other accompanying symptoms of fever, such as chills and discomfort.
Paracetamol uses in cough
Paracetamoll, is primarily used to reduce fever and relieve mild to moderate pain. While it may help alleviate discomfort associated with coughing, it does not directly target or treat the underlying causes of a cough.
Coughing is a natural reflex that helps clear the airways of irritants, mucus, or foreign substances. However, if a cough persists or is accompanied by severe symptoms, it is important to identify and address the underlying cause. Common causes of cough include respiratory infections (such as the common cold or flu), allergies, asthma, bronchitis, or even more serious conditions such as pneumonia.
In the case of a cough, it is generally more effective to focus on treating the underlying condition causing the cough rather than relying solely on paracetamol for symptom relief. Over-the-counter cough syrups or expectorants may be more appropriate to help alleviate cough symptoms by loosening mucus or suppressing the cough reflex.
It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance if you have a persistent or severe cough. They can help identify the cause of the cough and recommend appropriate treatment options based on your specific condition.
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, can be used to alleviate tooth pain on a temporary basis until you are able to see a dentist for proper evaluation and treatment. Here’s how paracetamol tablet can be used for tooth pain:
Pain relief: Paracetamol has analgesic properties and can help reduce mild to moderate tooth pain. It works by blocking certain pain signals in the brain.
Fever reduction: Tooth pain can sometimes be accompanied by fever. Paracetamol can help reduce fever if present along with tooth pain.
It’s important to note that paracetamol provides temporary relief and does not treat the underlying cause of the tooth pain. If you are experiencing tooth pain, it is advisable to schedule an appointment with a dentist as soon as possible to identify and address the underlying issue.
Additionally, follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the appropriate dosage based on your age, weight, and overall health condition. It’s essential to use paracetamol responsibly and avoid exceeding the recommended dosage to prevent potential adverse effects.
Please remember that this information is not a substitute for professional dental advice, and it’s important to consult a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment of tooth pain.
Paracetamol tablet uses in pregnancy
The use of paracetamol during pregnancy is generally considered safe when used at the recommended doses. Paracetamol is commonly used to relieve pain and reduce fever in pregnant women. However, it’s always important to consult with a healthcare professional or your obstetrician before taking any medication during pregnancy, including paracetamol.
Here are some key points to consider regarding paracetamol use during pregnancy:
Pain relief: Paracetamol can be used to alleviate mild to moderate pain during pregnancy, such as headaches, muscle aches, or toothaches. It is often recommended as the first-line treatment for pain relief in pregnant women.
Fever reduction: Paracetamol is also effective in reducing fever, which can sometimes occur during pregnancy due to various reasons. Reducing fever is important to maintain the mother’s comfort and prevent any potential complications.
Recommended dosage: When using paracetamol during pregnancy, it’s important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines provided by your healthcare professional or the instructions on the packaging. It is typically considered safe when used at the recommended doses.
Avoid excessive use: It’s crucial to avoid excessive or prolonged use of paracetamol during pregnancy, especially at higher doses than recommended. Taking excessive amounts of paracetamol for an extended period can potentially have adverse effects on the mother and the developing fetus.
Seek medical advice: If you have any concerns or questions about using paracetamol or any other medication during pregnancy, it is always best to consult with your healthcare professional or obstetrician. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation and guide you on the appropriate use of medications.
Remember that each pregnancy is unique, and individual circumstances may vary. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure the safe and appropriate use of any medication during pregnancy.
Paracetamol tablet uses in chronic diseases
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is commonly used for pain relief and fever reduction. However, its use in chronic diseases should be approached with caution, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Here are a few considerations regarding the use of paracetamol tablets in chronic diseases:
Liver disease: Paracetamol is primarily metabolized in the liver, so individuals with liver disease or impaired liver function should use paracetamol with caution. Excessive or prolonged use of high doses can potentially cause liver damage. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate guidance.
Kidney disease: Paracetamol is generally considered safe for individuals with kidney disease when used at recommended doses. However, individuals with severe kidney disease or on dialysis should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor kidney function.
Cardiovascular disease: Paracetamol is typically considered safe for individuals with cardiovascular disease. However, certain formulations of paracetamol, such as combination products containing other ingredients like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may have cardiovascular risks. It’s important to read the product label and consult with a healthcare professional before using combination medications.
Other chronic conditions: Paracetamol can be used for pain relief in various chronic conditions, such as arthritis or chronic back pain. However, it is essential to consider any potential interactions with other medications being taken for the specific chronic condition. It’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure the safe and appropriate use of paracetamol in conjunction with other treatments.
In general, it’s important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any specific chronic disease or condition. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health situation and help you determine the appropriate use of paracetamol or other medications.
Paracetamol tablet uses for head ache
Paracetamol is most commonly used for the relief of headache. It is effective in reducing mild to moderate pain, including headaches. Here’s how paracetamol tablets can be used for headache:
Pain relief: Paracetamol works by blocking certain pain signals in the brain, helping to alleviate headache pain. It is particularly effective for tension headaches and mild migraines.
Fever reduction: Paracetamol also has antipyretic properties, which means it can help reduce fever that may sometimes accompany certain types of headaches.
Here are a few important considerations when using paracetamol for headaches:
Dosage: It’s important to follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate dosing based on your age, weight, and overall health condition.
Combination medications: Paracetamol is often available in combination with other active ingredients, such as caffeine or aspirin. These combination products may provide additional benefits for specific types of headaches, but it’s important to read the product label and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable option for your specific headache type.
Caution with other medications: If you are taking other medications or have any underlying health conditions, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist to ensure that paracetamol does not interact with any other medications you are currently taking.
It’s important to note that while paracetamol can help provide temporary relief from headache pain, it does not address the underlying causes of recurrent or severe headaches. If you experience frequent or severe headaches, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Caution 🙏 Pleas eremember that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have specific concerns or questions about using paracetamol for headaches, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance
Use of paracetamol for periods/Menstrual Stomach Pain
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) can be used to alleviate pain associated with menstrual periods, such as menstrual cramps or discomfort. Here’s how paracetamol can be used for period pain:
Pain relief: Paracetamol is an effective analgesic and can help reduce mild to moderate pain commonly experienced during menstrual periods. It works by blocking certain pain signals in the brain.
Menstrual cramps: Paracetamol can help alleviate menstrual cramps, also known as dysmenorrhea. These cramps are caused by the release of certain chemicals called prostaglandins, which cause the uterus to contract. Paracetamol can help reduce the intensity of these cramps and provide relief.
When using paracetamol for period pain, it’s important to follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a healthcare professional. It’s generally advisable to start taking paracetamol as soon as the symptoms begin and continue as necessary, while not exceeding the recommended dosage.
It’s worth noting that if you consistently experience severe menstrual pain that significantly affects your daily activities or quality of life, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help assess your symptoms, rule out any underlying conditions, and provide appropriate management options.
Remember, while paracetamol can help alleviate period pain, it does not address the underlying cause of menstrual discomfort. It is important to practice good self-care during your menstrual cycle, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, applying heat to the abdomen, and practicing relaxation techniques.
Conclusion
In summary, Paracetamol is a versatile medication used for pain relief, fever reduction, managing cold
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is a widely used medication with several applications. Here are some common uses of paracetamol:
- Pain relief: Paracetamol is commonly used to alleviate mild to moderate pain, including headaches, toothaches, muscle aches, back pain, and menstrual pain.
- Fever reduction: Paracetamol is effective in reducing fever, making it useful for managing fever associated with illnesses such as the common cold, flu, or other infections.
- Cold and flu symptoms: Paracetamol can help relieve symptoms commonly experienced during cold and flu, such as headache, sore throat, and body aches.
- Post-vaccination discomfort: Paracetamol is sometimes recommended for managing pain or discomfort at the injection site following certain vaccinations.
If you have any concerns or questions about using paracetamol for pain or need further guidance, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice