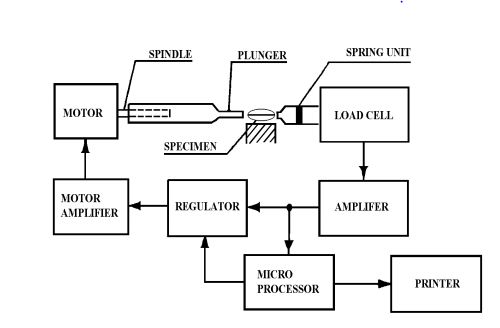
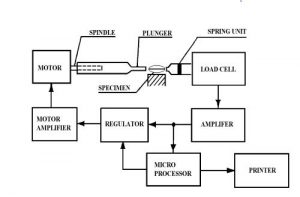
-
B Pharmacy First Year Syllabus
Bachelor of Pharmacy is one of the finest educations at this point in time. Every year zillions of students are joining B. Pharmacy to study Pharmacy. It is a degree of three years that is studied semester wise. It is an under graduation degree that gives the under graduation certification to the students. It is the next level of education after intermediate. Students who have studied intermediate with Bi.Pc background will go for under graduation into B. Pharmacy course. It is a study about art and science. The candidates of Pharmacy will be eligible to invent new drugs by performing researches in the labs.
Students of Pharmacy will be able to get theoretical knowledge along with practical knowledge as they perform various experiments while preparing new drugs for various diseases. Pharmacy Council of India (PCI) is responsible to manage Pharmacy graduate level education in the entire country. It is a statutory body that is governed by the provisions of the Pharmacy Act, 1948 that was passed by the Indian Parliament.
- Pharmacy first year
Students from various streams of intermediate like Physics, Chemistry, Maths, or Physics, Chemistry, Biology or Physics, Chemistry, Maths and Biology subjects are eligible to go for B. Pharmacy under graduation for three years. They need to take entrance test in order to study B. Pharmacy. B. Pharmacy is a semester wise education where the semester system is different from state to state. Students will need to take various entrance examinations in order to join B. Pharmacy. The entrance examinations to enter B. Pharmacy include B Pharma Entrance Exam, GPAT – Graduate Pharmacy Aptitude Test, MHT-CET Maharashtra Common Entrance Test etc.
Candidates can work in various areas of discipline like chemist shops, drug control administration, educational institutes, food and drug administration, health centers, hospitals, medical dispensing store, pharmaceutical firms, research agencies, sales and marketing departments etc.
-
Pharmacy First Year Subjects
The subjects in B. Pharmacy first year includes:
-
Remedial Mathematical Biology
-
Advanced Mathematics
-
Anatomy
-
Physiology and Health Education
-
Physical Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Physical Pharmacy
-
Basic Electronics and Computer Applications
-
Pharmaceutical Analysis
-
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry
-
Pharmacognosy
These are the list of subjects that needs to be studied in the first year of B. Pharmacy. Few state Pharmacy institutes will schedule the B. Pharmacy first year to be held semester wise while few institutes will schedule the B. Pharmacy for an entire year. The above subjects will be studied in the first year of B. Pharmacy. Students need to clear all the subjects in order to get promoted to second year of Pharmacy. Qualified candidates from B. Pharmacy are eligible to take Masters Degree.
-
B. Pharmacy First Year Syllabus
The Syllabi of Bachelor of Pharmaceutical Sciences includes 11 subjects of total. It includes both theory and practicals. The syllabus will be divided into two sections. The first section of B. Pharmacy includes various topics and contents related to pharma.
Pharmaceutics
Section – I
- Introduction to Pharmaceutics and its scope
- Definition of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutics, Area of Pharmaceutics, Physical Pharmacy, Biopharmaceutics, Pharmaceutical Technology, Microbilogy, Dispensing and Pharmacy Practices, Historical background and development of profession of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical industry in India.
- Introduction to pharmacopoeias and other compendia.
- Definition of drug, New Drug as per D&C Act 1940, steps for New Drug Development – filing of INDA, clinical research, filing of NDA.
- Brief Introduction to Good Manufacturing Practices & Quality Assurance
- Introduction to Dosage forms
- Classification of the basis of nature, routes of administration, concept of new drug delivery system sustained release and targeted drug delivery system with some examples.
- Concept of Pre-formulations and formulation- introductory aspects of physicochemical properties with their application, types of additives with examples.
- Concept of Bio-availability, Bioequivalence, Biopharmaceutics, Absorption, and Mechanism of absorption. Concept of drug distribution, Concept of drug metabolism and concept of drug excretion. Drug efficiency and dose response concept. Physiological consideration of various routes of administration.
- Radiopharmaceuticals: Radioactivity, Production and Quality control of radiopharmaceuticals.
- Packaging: Containers, closures, and materials for them, until dose packing.
- Alternative systems of medicine: Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Unani and Siddha.
Section –II
- Solution – Definition, factors affecting rate of solution, methods used to improve solubility and preformulation studies. Types of ingredients used during formulation. Manufacturing processes involved in liquid oral preparation. Evaluation including control on raw materials, in process control and finished Product controls. Formulation – syrups, elixirs, aromatic water, linctuses, ENT preparations and pains, mouth washes.
- Equipments used in manufacturing and packing of oral solution, liquid mixing mechanism of mixing, impeller, propeller mixers, paddle mixer, baffles, prevention of aeration and foam.
- Filtration and Clarification.
- Size Reducation
- Size Separation
- Powders
- Granule manufacturing as a dosage form
Subjects for 1st year (Semester 1)
| Subjects | Theory | Practical | ||
| Hours | Marks | Hours | Marks | |
| HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-I | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| PHARMACEUTICS- I | 45 | 100 | 3/week | 50 |
| PHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| COMMUNICATION SKILLS* | 30 | 50 | 2/week | 25 |
| REMEDIAL BIOLOGY*/ REMEDIAL MATHEMATICS(Only theory)* | 30 | 50 | 30 | 25 |
| Total marks | 675/725 $/750# | |||
#Applicable ONLY for the students who have studied Mathematics / Physics / Chemistry at HSC and appearing for Remedial Biology (RB) course.
$Applicable ONLY for the students who have studied Physics / Chemistry / Botany / Zoology at HSC and appearing for Remedial Mathematics (RM) course.
* Non University Examination (NUE)
Syllabus for 1st Semester
| Subjects | Syllabus | |
| Theory | Practical | |
|
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-I |
Unit I(Introduction to human body, Cellular level of organization, Tissue level of organization); Unit II(Integumentary system, Skeletal system, Joints); Unit III(Body fluids and blood, Lymphatic system); Unit IV(Peripheral nervous system, Peripheral nervous system); Unit V (Cardiovascular system) | 1. Study of compound microscope. 2. Microscopic study of epithelial and connective tissue 3. Microscopic study of muscular and nervous tissue 4. Identification of axial bones 5. Identification of appendicular bones 6. Introduction to hemocytometry. 7. Enumeration of white blood cell (WBC) count 8. Enumeration of total red blood corpuscles (RBC) counts 9. Determination of bleeding time 10. Determination of clotting time 11. Estimation of hemoglobin content 12. Determination of blood group. 13. Determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). 14. Determination of heart rate and pulse rate. 15. Recording of blood pressure. |
|
PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS |
Unit I(Pharmaceutical analysis, Errors, Pharmacopoeia); Unit II(Acid base titration, Non aqueous titration); Unit III(Precipitation titration, Complexometric titration, Gravimetry, Basic Principles,methods and application of diazotisation titration); Unit IV(Redox titrations); Unit V(Electrochemical methods of analysis- Conductometry, Potentiometry, Polarography) | Limit Tests- (1) Chloride (2) Sulphate (3) Iron (4) Arsenic; Preparation and standardization of -(1) Sodium hydroxide (2) Sulphuric acid (3) Sodium thiosulfate (4) Potassium permanganate (5) Ceric ammonium sulphate; Assay of the following compounds along with Standardization of Titrant- (1) Ammonium chloride by acid base titration (2) Ferrous sulphate by Cerimetry (3) Copper sulphate by Iodometry (4) Calcium gluconate by complexometry (5) Hydrogen peroxide by Permanganometry (6) Sodium benzoate by non-aqueous titration (7) Sodium Chloride by precipitation titration; Determination of Normality by electro-analytical methods – (1) Conductometric titration of strong acid against strong base (2) Conductometric titration of strong acid and weak acid against strong base (3) Potentiometric titration of strong acid against strong base |
|
PHARMACEUTICS- I |
Unit I(Historical background and development of profession of pharmacy, Prescription, Dosage forms, Posology); Unit II(Pharmaceutical calculations, Powders, Liquid dosage forms); Unit III(Monophasic liquids, Biphasic liquids Suspensions, Emulsions); Unit IV(Suppositories, Pharmaceutical incompatibilities); Unit V-Semisolid dosage forms | 1. Syrups a) Syrup IP’66 b) Compound syrup of Ferrous Phosphate BPC’68 2. Elixirs a) Piperazine citrate elixir b) Paracetamol pediatric elixir 3.Linctus a) Terpin Hydrate Linctus IP’66 4. Solutions b) Iodine Throat Paint (Mandles Paint) a) Strong solution of ammonium acetate b) Cresol with soap solution c) Lugol’s solution 5. Suspensions a) Calamine lotion b) Magnesium Hydroxide mixture c) Aluminimum Hydroxide gel 6. Emulsions a) Turpentine Liniment b) Liquid paraffin emulsion 7. Powders and Granules a) ORS powder (WHO) b) Effervescent granules c)Dusting powder d)Divded powders 8. Suppositories a) Glycero gelatin suppository b) Coca butter suppository c) Zinc Oxide suppository 8. Semisolids a) Sulphur ointment b) Non staining-iodine ointment with methyl salicylate c) Carbopal gel 9. Gargles and Mouthwashes a) Iodine gargle b) Chlorhexidine mouthwash |
|
PHARMACEUTICAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY |
Unit I(Impurities in pharmaceutical substances, General methods of preparation of compounds); Unit II(Acids, Bases and Buffers, Major extra and intracellular electrolytes, Dental products); Unit III(Gastrointestinal agents, Acidifiers, Antacid, Cathartics, Antimicrobials); Unit IV(Miscellaneous compounds, Expectorants, Emetics, Haematinics, Poison and Antidote, Astringents); Unit V- Radiopharmaceuticals | 1.Limit tests for following ions(Chlorides and Sulphates Modified limit test for Chlorides and Sulphates Limit test for Iron Limit test for Heavy metals Limit test for Lead Limit test for Arsenic) 2. Identification test Magnesium hydroxide Ferrous sulphate Sodium bicarbonate Calcium gluconate Copper sulphate 3.Test for purity Swelling power of Bentonite Neutralizing capacity of aluminum hydroxide gel Determination of potassium iodate and iodine in potassium Iodide 4.Preparation of inorganic pharmaceuticals Boric acid Potash alum Ferrous sulphate |
|
COMMUNICATION SKILLS |
Unit I(Communication Skills, Barriers to communication, Perspectives in Communication); Unit II(Elements of Communication, Communication Styles); Unit III(Basic Listening Skills, Effective Written Communication, Writing Effectively); Unit IV(Interview Skills, Giving Presentations); Unit V- Group Discussion | Basic communications covering the following topics -Meeting People Asking Questions Making Friends What did you do? Do’s and Don’ts; Pronunciations covering the following topics- Pronunciation (Consonant Sounds) Pronunciation and Nouns Pronunciation (Vowel Sounds); Advanced Learning Listening Comprehension / Direct and Indirect Speech Figures of Speech Effective Communication Writing Skills Effective Writing Interview Handling Skills E-Mail etiquette Presentation Skills |
|
REMEDIALBIOLOGY |
Unit I(Living world, Morphology of Flowering plants); Unit II(Body fluids and circulation, Digestion and Absorption, Breathing and respiration); Unit III(Excretory products and their elimination, Neural control and coordination, Chemical coordination and regulation, Human reproduction); Unit IV(Plants and mineral nutrition, Photosynthesis); Unit V(Plant respiration, Plant growth and development, Cell – The unit of life, Tissues | 1. Introduction to experiments in biology a) Study of Microscope b) Section cutting techniques c) Mounting and staining d) Permanent slide preparation 2. Study of cell and its inclusions 3. Study of Stem, Root, Leaf, seed, fruit, flower and their modifications 4. Detailed study of frog by using computer models 5. Microscopic study and identification of tissues pertinent to Stem, Root Leaf, seed, fruit and flower 6. Identification of bones 7. Determination of blood group 8. Determination of blood pressure 9. Determination of tidal volume |
| REMEDIAL MATHEMATICS | Unit I(Partial fraction, Logarithms, Function, Limits and continuity); Unit II(Matrices and Determinant); Unit III(Calculus –Differentiation); Unit IV(Analytical Geometry- Introduction, Straight Line, Integration); Unit V(Differential Equations-Application in solving Pharmacokinetic equations, Laplace Transform- Application in solving Chemical kinetics and Pharmacokinetics equations) | |
Subjects for Semester 2
| Subjects | Theory | Practical | ||
| Hours | Marks | Hours | Marks | |
| HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-II | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| BIOCHEMISTRY | 45 | 100 | 4/week | 50 |
| PATHOPHYSIOLOGY | 45 | 100 | – | – |
| COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN PHARMACY* | 30 | 75 | – | 25 |
| ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES* | 30 | 75 | – | – |
| Total marks | 725 | |||
* The subject experts at college level shall conduct examinations
Syllabus for Semester 2
| Subjects | Syllabus | |
| Theory | Practical | |
|
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-II |
Unit I- Nervous system (Organization of nervous system, neuron, neuroglia, classification and properties of nerve fibre, electrophysiology, action potential, nerve impulse, receptors, synapse, neurotransmitters. Central nervous system: Meninges, ventricles of brain and cerebrospinal fluid, structure and functions of brain (cerebrum, brain stem, cerebellum), spinal cord (gross structure, functions of afferent and efferent nerve tracts, reflex activity) ); Unit II- Digestive system (Anatomy of GI Tract with special reference to anatomy and functions of stomach, Acid production in the stomach, regulation of acid production through parasympathetic nervous system, pepsin role in protein digestion) small intestine 54 and large intestine, anatomy and functions of salivary glands, pancreas and liver, movements of GIT, digestion and absorption of nutrients and disorders of GIT. Energetics-Formation and role of ATP, Creatinine Phosphate and BMR) ;Unit III- Respiratory system (Anatomy of respiratory system with special reference to anatomy of lungs, mechanism of respiration, regulation of respiration Lung Volumes and capacities transport of respiratory gases, artificial respiration, and resuscitation methods), Urinary system (Anatomy of urinary tract with special reference to anatomy of kidney and nephrons, functions of kidney and urinary tract, physiology of urine formation, micturition reflex and role of kidneys in acid base balance, role of RAS in kidney and disorders of kidney); Unit IV- Endocrine system (Classification of hormones, mechanism of hormone action, structure and functions of pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, pineal gland, thymus and their disorders.); Unit V- Reproductive system (Anatomy of male and female reproductive system, Functions of male and female reproductive system, sex hormones, physiology of menstruation, fertilization, spermatogenesis, oogenesis, pregnancy and parturition), Introduction to genetics Chromosomes, genes and DNA, protein synthesis, genetic pattern of inheritance | 1. To study the integumentary and special senses using specimen, models, etc., 2. To study the nervous system using specimen, models, etc., 3. To study the endocrine system using specimen, models, etc 4. To demonstrate the general neurological examination 5. To demonstrate the function of olfactory nerve 6. To examine the different types of taste. 7. To demonstrate the visual acuity 8. To demonstrate the reflex activity 9. Recording of body temperature 10. To demonstrate positive and negative feedback mechanism. 11. Determination of tidal volume and vital capacity. 12. Study of digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular systems, urinary and reproductive systems with the help of models, charts and specimens. 13. Recording of basal mass index. 14. Study of family planning devices and pregnancy diagnosis test. 15. Demonstration of total blood count by cell analyser 16. Permanent slides of vital organs and gonads |
|
PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY –I |
Unit I- Classification, nomenclature and isomerism, Classification of Organic Compounds Common and IUPAC systems of nomenclature of organic compounds (up to 10 Carbons open chain and carbocyclic compounds) Structural isomerisms in organic compounds); Unit II- Alkanes*, Alkenes* and Conjugated dienes* (SP3 hybridization in alkanes, Halogenation of alkanes, uses of paraffins. Stabilities of alkenes, SP2 hybridization in alkenes E1 and E2 reactions – kinetics, order of reactivity of alkyl halides, rearrangement of carbocations, Saytzeffs orientation and evidences. E1 verses E2 reactions, Factors affecting E1 and E2 reactions. Ozonolysis, electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes, Markownikoff’s orientation, free radical addition reactions of alkenes, Anti Markownikoff’s orientation. Stability of conjugated dienes, Diel-Alder, electrophilic addition, free radical addition reactions of conjugated dienes, allylic rearrangement); Unit III- Alkyl halides* (SN1 and SN2 reactions – kinetics, order of reactivity of alkyl halides, stereochemistry and rearrangement of carbocations. SN1 versus SN2 reactions, Factors affecting SN1 and SN2 reactions, Structure and uses of ethylchloride, Chloroform, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, dichloromethane, tetrachloromethane and iodoform), Alcohols*( Qualitative tests, Structure and uses of Ethyl alcohol, Methyl alcohol, chlorobutanol, Cetosteryl alcohol, Benzyl alcohol, Glycerol, Propylene glycol); Unit IV- Carbonyl compounds* (Aldehydes and ketones) Nucleophilic addition, Electromeric effect, aldol condensation, Crossed Aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction, Crossed Cannizzaro reaction, Benzoin condensation, Perkin condensation, qualitative tests, Structure and uses of Formaldehyde, Paraldehyde, Acetone, Chloral hydrate, Hexamine, Benzaldehyde, Vanilin, Cinnamaldehyde); Unit V- Carboxylic acids* (Acidity of carboxylic acids, effect of substituents on acidity, inductive effect and qualitative tests for carboxylic acids ,amide and ester Structure and Uses of Acetic acid, Lactic acid, Tartaric acid, Citric acid, Succinic acid. Oxalic acid, Salicylic acid, Benzoic acid, Benzyl benzoate, Dimethyl phthalate, Methyl salicylate and Acetyl salicylic acid), Aliphatic amines* – Basicity, effect of substituent on Basicity. Qualitative test, Structure and uses of Ethanolamine, Ethylenediamine, Amphetamine) | I. Systematic qualitative analysis of unknown organic compounds like
1. Preliminary test: Color, odour, aliphatic/aromatic compounds, saturation and unsaturation, etc. 2. Detection of elements like Nitrogen, Sulphur and Halogen by Lassaigne’s test 3. Solubility test 4. Functional group test like Phenols, Amides/ Urea, Carbohydrates, Amines, Carboxylic acids, Aldehydes and Ketones, Alcohols, Esters, Aromatic and Halogenated Hydrocarbons, Nitro compounds and Anilides. 5. Melting point/Boiling point of organic compounds 6. Identification of the unknown compound from the literature using melting point/ boiling point. 7. Preparation of the derivatives and confirmation of the unknown compound by melting point/ boiling point. 8. Minimum 5 unknown organic compounds to be analysed systematically; II- Preparation of suitable solid derivatives from organic compounds; III. Construction of molecular models |
|
BIOCHEMISTRY |
Unit I– Biomolecules (Introduction, classification, chemical nature and biological role of carbohydrate, lipids, nucleic acids, amino acids and proteins), Bioenergetics (Concept of free energy, endergonic and exergonic reaction, Relationship between free energy, enthalpy and entropy; Redox potential. Energy rich compounds; classification; biological significances of ATP and cyclic AMP) ; Unit II- Carbohydrate metabolism(Glycolysis – Pathway, energetics and significance,Citric acid cycle- Pathway, energetics and significance, HMP shunt and its significance, Glucose-6-Phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, Glycogen metabolism Pathways and glycogen storage diseases (GSD), Gluconeogenesis- Pathway and its significance, Hormonal regulation of blood glucose level and Diabetes mellitus), Biological oxidation(Electron transport chain (ETC) and its mechanism. Oxidative phosphorylation & its mechanism and substrate phosphorylation, Inhibitors ETC and oxidative phosphorylation/Uncouplers.); Unit III –Lipid metabolism(β-Oxidation of saturated fatty acid (Palmitic acid), Formation and utilization of ketone bodies, ketoacidosis
De novo synthesis of fatty acids (Palmitic acid), Biological significance of cholesterol and conversion of cholesterol into bile acids, steroid hormone and vitamin D,Disorders of lipid metabolism: Hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, fatty liver and obesity.) Amino acid metabolism (General reactions of amino acid metabolism: Transamination, deamination & decarboxylation, urea cycle and its disorders, Catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine and their metabolic disorders(Phenyketonuria, Albinism, alkeptonuria, tyrosinemia), Synthesis and significance of biological substances; 5-HT, melatonin, dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline, Catabolism of heme; hyperbilirubinemia and jaundi); Unit IV- Nucleic acid metabolism and genetic information transfer (Biosynthesis of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, Catabolism of purine nucleotides and Hyperuricemia and Gout disease, Organization of mammalian genome, Structure of DNA and RNA and their functions, DNA replication (semi conservative model), Transcription or RNA synthesis Genetic code, Translation or Protein synthesis and inhibitors); Unit V- Enzymes (Introduction, properties, nomenclature and IUB classification of enzymes, Enzyme kinetics (Michaelis plot, Line Weaver Burke plot) Enzyme inhibitors with examples, Regulation of enzymes: enzyme induction and repression, allosteric enzymes regulation, Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of enzymes and isoenzymes, Coenzymes –Structure and biochemical functions) |
1. Qualitative analysis of carbohydrates (Glucose, Fructose, Lactose, Maltose,Sucrose and starch)
2. Identification tests for Proteins (albumin and Casein) 3. Quantitative analysis of reducing sugars (DNSA method) and Proteins (Biuret method) 4. Qualitative analysis of urine for abnormal constituents 5. Determination of blood creatinine 6. Determination of blood sugar 7. Determination of serum total cholesterol 8. Preparation of buffer solution and measurement of pH 9. Study of enzymatic hydrolysis of starch 10. Determination of Salivary amylase activity 11. Study the effect of Temperature on Salivary amylase activity 12. Study the effect of substrate concentration on salivary amylase activity. |
| PATHOPHYSIOLOGY | Unit I – Basic principles of Cell injury and Adaptation:
(Introduction, definitions, Homeostasis, Components and Types of Feedback systems, Causes of cellular injury, Pathogenesis (Cell membrane damage, Mitochondrial damage, Ribosome damage, Nuclear damage),Morphology of cell injury – Adaptive changes (Atrophy, Hypertrophy, hyperplasia, Metaplasia, Dysplasia),Cell swelling, Intra cellular accumulation, Calcification, Enzyme leakage and Cell Death Acidosis & Alkalosis, Electrolyte imbalance), Basic mechanism involved in the process of inflammation and repair: (Introduction, Clinical signs of inflammation, Different types of Inflammation, Mechanism of Inflammation – Alteration in vascular permeability and blood flow, migration of WBC’s, Mediators of inflammation, Basic principles of wound healing in the skin, Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis); Unit II– Cardiovascular System: (Hypertension, congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease (angina, myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis), Respiratory system: (Asthma, Chronic obstructive airways diseases.), Renal system: (Acute and chronic renal failure.) Unit III- Haematological Diseases: (Iron deficiency, megaloblastic anemia (Vit B12 and folic acid), sickle cell anemia, thalasemia, hereditary acquired anemia, haemophilia), Endocrine system: (Diabetes, thyroid diseases, disorders of sex hormones.), Nervous system: (Epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, psychiatric disorders: Depression, schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease.), Gastrointestinal system: (Peptic Ulcer), Unit IV– Inflammatory bowel diseases, jaundice, hepatitis (A,B,C,D,E,F) alcoholic liver Disease, Disease of bones and joints: (Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis and gout), Principles of cancer: (classification, etiology and pathogenesis of cancer), Diseases of bones and joints: (Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout), Principles of Cancer: (Classification, etiology and pathogenesis of Cancer) Unit V- Infectious diseases: (Meningitis, Typhoid, Leprosy, Tuberculosis, Urinary tract infections), Sexually transmitted diseases: (AIDS, Syphilis, Gonorrhea) |
_ |
| COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN PHARMACY | Unit IV- Number system: (Binary number system, Decimal number system, Octal
number system, Hexadecimal number systems, conversion decimal to binary, binary to decimal, octal to binary etc, binary addition, binary subtraction – One’s complement ,Two’s complement method, binary multiplication, binary division.), Concept of Information Systems and Software : (Information gathering, requirement and feasibility analysis, data flow diagrams, process specifications, input/output design, process life cycle, planning and managing the project.); Unit II- Web technologies: (Introduction to HTML, XML,CSS and Programming languages, introduction to web servers and Server Products, Introduction to databases, MYSQL, MS ACCESS, Pharmacy Drug database.); Unit III- Application of computers in Pharmacy (Drug information storage and retrieval, Pharmacokinetics, Mathematical model in Drug design, Hospital and Clinical Pharmacy, Electronic Prescribing and discharge (EP) systems, barcode medicine identification and automated dispensing of drugs, mobile technology and adherence monitoring, Diagnostic System, Lab-diagnostic System, Patient Monitoring System, Pharma Information System); Unit IV- Bioinformatics: (Introduction, Objective of Bioinformatics, Bioinformatics Databases, Concept of Bioinformatics, Impact of Bioinformatics in Vaccine Discovery) Unit-V Computers as data analysis in Preclinical development: (Chromatographic dada analysis(CDS), Laboratory Information management System (LIMS) and Text Information Management System(TIMS)) |
1. Design a questionnaire using a word processing package to gather information about a particular disease.
2. Create a HTML web page to show personal information. 3. Retrieve the information of a drug and its adverse effects using online tools 4 Creating mailing labels Using Label Wizard , generating label in MS WORD 5. Create a database in MS Access to store the patient information with the required fields Using access 6. Design a form in MS Access to view, add, delete and modify the patient record in the database 7. Generating report and printing the report from patient database 8. Creating invoice table using – MS Access 9. Drug information storage and retrieval using MS Access 10. Creating and working with queries in MS Access 11. Exporting Tables, Queries, Forms and Reports to web pages 12. Exporting Tables, Queries, Forms and Reports to XML pages |
| ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | Unit-I:The Multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies
Natural Resources (Renewable and non-renewable resources: Natural resources and associated problems a) Forest resources; b) Water resources; c) Mineral resources; d) Food resources; e) Energy resources; f) Land resources: Role of an individual inconservation of natural resources.); Unit II: Ecosystems § Concept of an ecosystem. § Structure and function of an ecosystem. § Introduction, types, characteristic features, structure and function of the ecosystems: Forest ecosystem; Grassland ecosystem; Desert ecosystem; Aquatic ecosystems (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries); Unit- III: Environmental Pollution: Air pollution; Water pollution; Soil pollution. |
_ |