Here is a great article for our readers especially D Pharmacy 1st Year B Pharm First Sem students who are struggling to learn Anatomy & Physiology Subjects. Hence we provide Notes as Solved Question Paper which are very important for your examinations.
Give functions of mitochondria & endoplasmic reticulum. (1 mark each)
Mitochondria is known as power house of cell. They are involved in cellular respiration, the process by which chemical energy is made available in the cell. When nutrients and oxygen come in contact with the oxidative enzymes of mitochondria, they combine to form CO2, water & energy, this is in the form of ATP. (aerobic oxidation)
- Endoplasmic reticulum are of two types. Smooth and rough. Smooth ER synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones and associated with detoxification of drugs. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes. It is a site of synthesis of proteins that are exported from
b) Define tissue. Classify connective tissue. (def. 1 mark, classification 1 mark)
10 Basic Definitions ofPharmacy
Groups of cells which have the same physical characteristics and similar functions are termed as tissues.
Classification of connective tissue:
- Connective tissue proper: i) Areolar tissu ii) Adipose tissue
iii) White fibrous tissue iv) Yellow elastic tissue
- Specialised connective tissue: i) Bone ii) Cartilage
- Vascular tissue: i) Blood ii) Lymphoid tissue
c) What are true ribs & false ribs? ( 2 marks)
There are 12 pairs of ribs. Anteriorly, the first seven pairs of ribs are attached to the sternum via costal cartilage & are known as true ribs. The next three ribs are attached indirectly via seventh rib & known as false ribs
d) Write composition of blood. (2 marks)
Composition
It is composed of a liquid matrix plasma (55%) & different cells suspended in it (45%).
Plasma- Composition– Water-90-92%, plasma proteins, inorganic salts, nutrients, waste material, hormones & gases.
Blood cells – Red blood cells or erythrocytes, white blood cells or leucocytes and platelets or thrombocytes
B.PHARMACY & M. PHARMACY PROJECTS
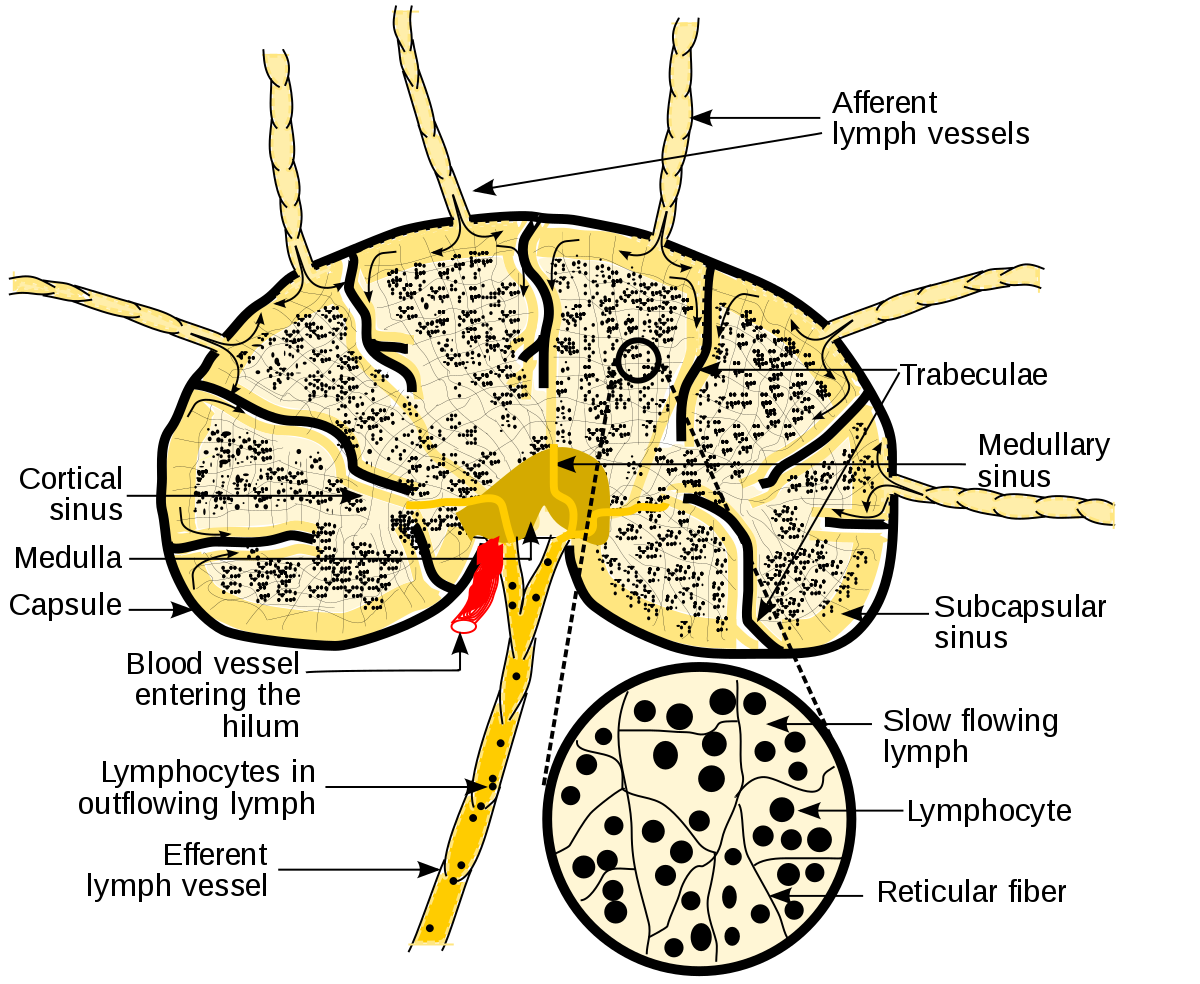
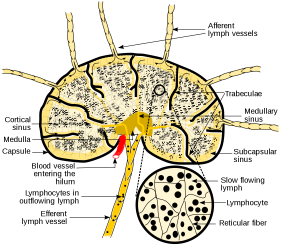
e) Draw and label lymph node
f) What is SA node & AV node? (1 mark each)
SA node (sinoatrial node) This is small mass of specialized neuromuscular cells in the walls of myocardium of right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava. It is known as pacemaker of the heart as it initiates the impulses.
AV node- (atrioventricular node): This is the mass of neuromuscular cells in the wall of the atrial septum near the AV valves. Normally it conducts the impulses that are originated by SA node. It is known as secondary pace maker as it generates the impulses when there is problem with SA node.
g) Give the functions of CSF. (4 functions, 2 marks)
- To support & protect brain & spinal
- Maintain uniform pressure around
- Acts as cushion & shock absorber
- Keeps brain & spinal cord
h) Define (any two) (each 1 mark)
Presbyopia: As a process of aging, the lens loses its elasticity; the distant objects are seen clear but close objects are
- Cataract: This is opacity of lens which may be age related or congenital bilateral or unilateral.
- Hypermetropia: Also known as farsightedness. Far vision is normal but close vision is blurred, because the near image is focused behind the retina as eye ball length is too short or due to flattened
i) Write the functions of hypothalamus. ( 2 marks)
- It controls the hormone release from pituitary
- Control of autonomic nervous system, appetite & satiety, thirst, body , emotions, sexual behavior & biological clock.
j) Name any two cranial nerves with their function. (Any 2, 2 marks)
Olfactory – sense of smell
Optic – sense of light/vision
Occulomotor – movement of the eyeball, change shape of lens, Constriction of pupil, raising the upper lid.
Trochlear – movement of the eye
Trigeminal – receives impulses of pain temp. & touch for face & head, stimulates muscle of mastication
Abducent – abduction of eye ball
Facial – conveys impulse from taste buds & supplies muscles of facial expression
Auditory (vestibulocochlear) – conveys impulses to the cerebellum for posture &
Balance & sense of hearing
Glossopharyngeal – Sense of taste, production of saliva and movement of
Pharynx
Vagus – Secretion, movement in organs
Accessory – Movements of head, shoulder, pharynx and larynx
Hypoglossal – Supplies to the muscle of tongue & muscle surrounding the hyoid bone & helps in swallowing & speech.
06
k) What are auditory ossicles? (1 mark) Write their function. (1 mark)
Auditory ossicles: Malleus, incus & stapes are the three small bones in the middle ear extending from tympanic membrane to the oval window. Sound vibrations of tympanic membrane are amplified & transmitted by these bones.
l) What is B.P.? Name the factors affecting B.P. (def 1 mark and any 4 factors 1 mark)
B.P is the force or lateral pressure which the blood exerts on the wall of blood vessels. Factors affecting B.P. are exercise, nutrition, age, stress, circulating hormones, autonomic nervous system activity.
Q2. Solve any four of the following: 12
- Define respiration. Write the process of external respiration. (def 1 mark, explanation 2 marks)
Respiration is a process of supply of oxygen present in atmosphere into the body & excretion for carbon dioxide.
External respiration- (cycle of breathing)
The normal human has 12-15 breath per min. Each breath consists of inspiration, expiration & pause.
Inspiration: The simultaneous contraction of intercostal muscles & diaphragm increases the capacity of thoracic cavity. This reduces the pressure in the lungs. To equalise the pressure the air from atmosphere enters the lungs. The process of inspiration is active as it needs energy for muscle contraction. It lasts for 2 sec.
Expiration: Relaxation of intercostal muscles & diaphragm results in decrease in the space in the lungs. As a result, the pressure inside the lungs increases as compared to atmospheric pressure. The air from the lungs is expelled from the lungs. This process is passive as does not require energy. The expiration lasts for 3 sec. After expiration there is pause & then the next cycle begins.
b) Write steps involved in urine formation. Describe selective reabsorption. (steps 1 mark, explanation 2 marks)
There are three processes of urine formation:
- Glomerular filtration
- Selective reabsorption
- Tubular secretion.
Selective reabsorption:
Selective reabsorption is the process by which the composition and volume of the glomerular filtrate is altered during its passage through the convoluted tubules, Loop of Henle and the collecting tubule. The purpose of this process is to reabsorb those constituents of the filtrate which are essential to the body, maintain the fluid and electrolyte balance and the alkalinity of blood.
Some constituents of the glomerular filtrate e.g. glucose; vitamins and amino acids get completely reabsorbed into the blood. These substances are called high- threshold substances.
Low-threshold substances like urea, uric acid are absorbed slightly.
Some substances e.g. creatinine are not at all absorbed.(no-threshold substances) Parathormone from parathyroid gland & calcitonin from thyroid gland regulate reabsorption of calcium & phosphate,
ADH from posterior pituitary increases the permeability of the tubule & increases water reabsorption.
Aldosterone by adrenal cortex increases reabsorption of sodium.
Pharmacology Notes: PPT PDF – ANTICANCER DRUGS
c)What is muscle tone? Give the functions of muscle. (muscle tone 1 mark, functions 2 marks)
Muscle tone is a sustained partial muscle contraction that allows maintenance of posture of the body.
08
Functions of the muscles are-
Skeletal muscles contract & help the movement of the body & stability of the joint. It also helps in generation of heat.Intercostal muscles help in respiration.
- Smooth muscles helps contraction & relaxation of blood vessels & controls blood flow & movement of the food in the alimentary
- Cardiac muscles help in the functioning of
d)Give the composition & function of gastric juice. (comp. 1 mark, functions 2 marks)
Composition of gastric juice:
Water, mineral salt, mucus, HCl, intrinsic factor, pepsinogen Functions of gastric juice-
- Water liquifies the food.
- HCl acidifies the food & stops the action of salivary
- HCl kills the
- Pepsinogen is activated to pepsin by HCl. This digests protein to smaller
- Intrinsic factor absorbs vit. B12 from small
- Mucus prevents mechanical injury to the stomach
e) Name hormones of adrenal cortex & mention their functions. (names 1 mark, functions 2 marks)
Adrenal cortex produces three groups of hormones namely glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoid & androgens.
Glucocorticoids: Cortisol or hydrocortisone is the main glucocorticoid. Others are corticosterone & cortisone.
They regulate metabolism like gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and proteolysis. Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone.) It regulates water & electrolyte balance. It increases the reabsorption of Na ions.
Androgens: The compounds secreted are insignificant to show any action.
f) Define reproduction. Name the different reproductive organs of male reproductive system. (def 1 mark, organs 2 marks)
Reproduction is the process of formation of offspring OR It is defined as process by which genetic material is passed from one generation to another & thus maintains continuation of species.
The male reproductive system consists of the following organs:
| Testis 2 | Epididymis | 2 | Spermatic cords | 2 | |
| Seminal vesicles | 2 | Ejaculatory ducts | 2 | Prostate gland | 1 |
| Urethra & Penis | 1 |
Q3. Solve any four of the following: 12
- Give differences between striated and smooth muscles. (any 6 points, 3 marks)
| Sr. No | Skeletal muscle | Smooth muscle |
| 1. | It is also known as striated Muscle | Non‐ striated muscle |
| 2. | It is less extensible | It is more extensible |
| 3. | The fibres (cell) are cylindrical and has
many nuclei |
The cells are spindle shaped
with only one central nucleus |
| 4. | They are under the control of our will. (voluntary) | They are not under the
control of our will.(involuntary) |
| 5. | The fibrous tissue enclosing
the whole muscle extends beyond the fibres to become the tendon which attaches the muscle to the bone or skin. |
Bundles of fibres form sheets of muscle. |
| 6. | There is distinct sarcolemma | No distinct sarcolemma |
| 7. | Present in tongue, arms or hands, legs,
etc |
Present in oesophagus, stomach,
intestine, etc |
b) Define: ( 1 mark each)
- Gout: Inflammation of joints due to deposition of sodium urate crystals in the joints.
- Arthritis: Chronic disease that results in pain and restricted movement of
- Sprain: Joint injury in which some of the fibres of supporting ligament are damaged OR If a ligament is stretched or torn; the injury is called a
c) Name different type of blood group. Explain the term universal donor and universal recipient. (name 1 mark, explanation 2 marks)
Different blood groups are: A, B, AB and O
Blood group “O” is called as Universal donor and Blood group “AB” is called as
Universal recipient.
Individuals have different antigens on the surface of their RBCs. These antigens determine their blood groups.
Blood group ‘O’ has neither A nor B antigen on their cell membrane. There will be no agglutination and thus blood can be safely transfused into A, B, AB and O. but can receive from only O.Therefore, blood group O is called universal donor.
Whereas blood group AB has neither antiA nor antiB antibodies. Transfusion of any group into these individuals is safe since there are no antibodies to react with them. But can donate only to AB. Hence it is called as universal recipient.
11
d) Define cardiac cycle. Write various events in cardiac cycle. (def 1 mark, explanation 2 marks)
Cardiac cycle: The events which occur in the heart during the circulation of blood during each heart beat is called cardiac cycle OR The series of events during one heart beat is known as cardiac cycle.
Events in cardiac cycle:
- Atrial systole (0.1 sec)
- Ventricular systole (0.3 sec)
- Complete cardiac diastole (0.4 sec)
Description of cardiac cycle (2 marks)
The superior & inferior vena cava transport the deoxygenated blood into right atrium. At the same time four pulmonary veins transport oxygenated blood into the left atrium. The impulses from the SA node spreads over the atria, atria contracts, the AV valves open and & blood flows to ventricles. ( atrial systole-0.1 sec)
When the wave of contraction reaches AV node, it is stimulated & emits impulses which spreads over AV bundle, bundle branches & purkinje fibres resulting in contraction of ventricles pumping the blood into pulmonary artery & the aorta. (ventricular systole 0.3 sec). After the contraction of the ventricles there is complete cardiac diastole(0.4 sec) when both atria & ventricles relax. After this the next cycle begins.
e) What is reflex action? Draw a well-labelled diagram of reflex arc. (Reflex action 1 ½ marks, diagram 1 ½ marks)
Reflex action is an automatic motor response given by the spinal cord to the sensory stimulus without involving brain in action. They are a part of defensive mechanisms of the body.
12
Important reflex actions are:
- Quick closing of an eyelid if eye is
- Sudden withdrawal of hand if fingers touch something
- Quick recovery of the balance of the body to prevent falling after a
- Sudden coughing attack if a food particle is
Diagram of reflex arc:
13
f) Mention layers of epidermis of skin. State functions of skin. ( names of layers 1 mark, any 4 functions 2 marks)
Layers of epidermis:
Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum and stratum granulosum & stratum germinativum Functions of skin:
- Protection – It forms the water proof layer & protects the inner delicate structures. It acts as the barrier against the invasion of the microbes, chemicals &dehydration. The melanin pigment protects against the harmful UV
- Regulation of body temp.- The temp. is constant at 36.8o When the metabolic rate of the body increases the body temp increases & vice versa. To ensure constant body temp, a balance between heat production & heat loss is maintained by the skin.
- Formation of vit. D.- 7-dehydroxycholesterol is present in the skin. The UV light from the sun converts it to vit.
- Sensation – It contains nerve endings of many sensory nerves which act as organ of sensation of touch, temp, pressure and
- Absorption- Some drugs & chemicals are absorbed through the
- Excretion- Skin is a minor excretory organ & excretes NaCl, urea & sub. like garlic.
Q4. Solve any four of the following: 12
- Define and give normal values: (1 mark for each)
- Tidal volume: It is the volume of air moved in & out of lungs during normal breathing. Normal value is 500
14
- Inspiratory reserve volume: It is the amount of air that can be breathed in and above the tidal volume by the deepest possible inspiration. Normal value is 1800 – 3000
- Residual volume: It is the volume of air remaining in lungs after forced Normal value is 1.2 L in males and 1.1 L in females.
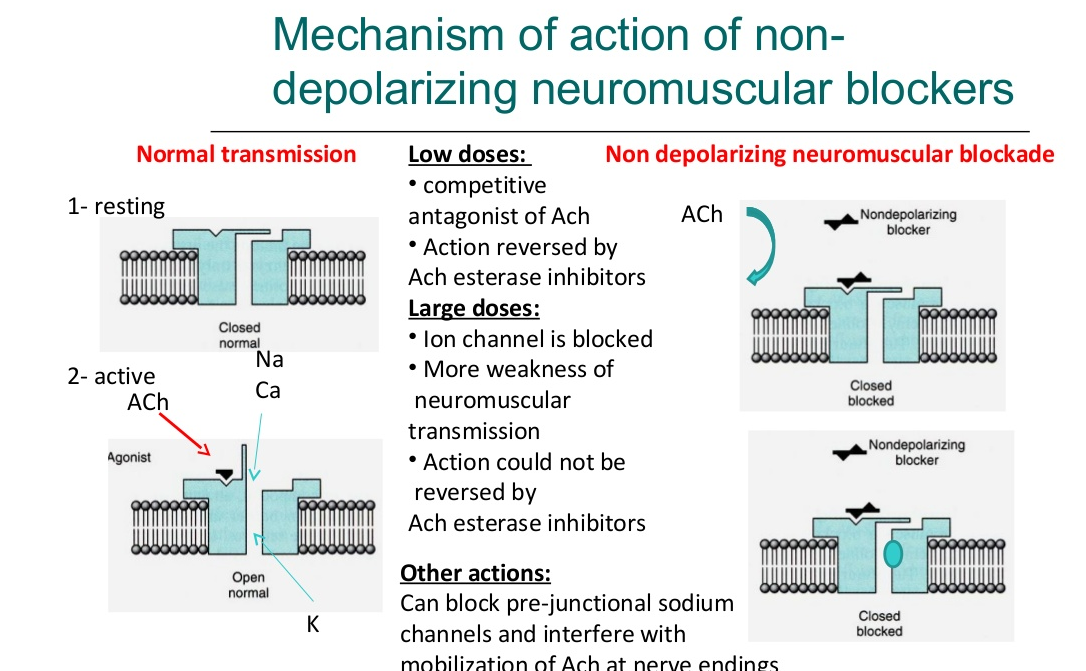
Give physiology of neuromuscular transmission. ( 3 marks)
When a nerve impulse reaches neuromuscular junction, passage of action potential over the sole feet causes the vesicles of acetylcholine to rupture into the synaptic cleft. The acetylcholine acts on the cell membrane to increase its permeability.
This allows spontaneous leakage of Na causing endplate potential. When the endplate potential increases, it stimulates the entire muscle fibre causing an action potential to travel in both directions along the fibre. When the action potential spread to inside of muscle fibre then Ca ions are released. This causes contraction of muscle fibres. Immediately after action potential is over, the previously released Ca ions recombine with reticulum and the muscle contraction stops.
The enzyme acetylcholinesterase present in the synaptic cleft. causes hydrolysis of acetylcholine. The muscle fibre is repolaised again to receive successive stimuli.
d) Describe the structure of stomach. ( str 2 marks, diag 1 mark)
Stomach is a J-shaped dilated portion of the alimentary canal. It is continuous with the oesophagus at cardiac sphincter and with duodenum at pyloric sphincter. It has 2 curvatures – lesser curvature and greater curvature. The stomach is divided into three regions- fundus, body & antrum. There are three layers of smooth muscle fibres outer longitudinal, the middle circular layer & the inner oblique fibres. This helps the churning movement & peristaltic movement.
16
Diagram
:
e) What is endocrine and exocrine gland? Name the endocrine glands. (each def 1 mark, any 4 endocrine glands 1 mark)
Endocrine glands are ductless glands which release their secretions (hormones) directly into the blood.
Exocrine gland: The glands that discharge their secretions through the duct are known as exocrine glands.
Endocrine glands: Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas (islets of Langerhans). adrenal glands, pineal gland, testes in male and ovaries in female.
17
f) Define menstruation. Explain proliferative phase of menstruation.(def 1 mark, explanation 2 marks)
Menstruation: This is the series of events occurring regularly in females every 26-30 days throughout the child bearing age. The cycle consists of menstrual phase for 4 days, proliferative phase for 10 days & secretary phase for 14 days.
Proliferative phase: It is characterized by release of oestrogen by the maturing ovarian follicle under the influence of FSH from the anterior pituitary. Oestrogen stimulates the proliferation of the endometrium in preparation of the fertilized ovum. The endometrium becomes thicker by rapid cell multiplication and this is accompanied by an increase in the number of mucus-secreting glands and blood capillaries. This phase lasts for 10 days and stops when ovulation occurs and oestrogen production is inhibited i.e. when the ovarian follicle ruptures.
Q.5 Solve any four of the following: (12 marks, 03 marks each)
- State the factors which accelerate and retard the clotting of blood. (3 marks, 1.5 marks each)
There are various factors which accelerate and retard the clotting of blood.
(1) Factors accelerating clotting are( any 3 points, 1.5 marks)
- During menstruation and parturition
- Injury to the walls of the blood vessels: An injury in the form of cut bleeds more freely than the injury by the
- The venom of viper snakes
- Higher temperature (above 46 0 C)
- Presence of calcium salts
18
(2) Factors retarding clotting are (any 3 points, 1.5 marks):
- In clinical condition like haemophilia, liver disease, afibrinogenemia, Christmas disease,
- Removal calcium ions from the blood by addition of sodium or potassium or citrate
ions.
(c ) Calcium deficiency in blood
(d)Lower temperature: However, lower temperature causes contraction of blood vessels. ( e)Deficiency of vitamin K
(b) Describe how circulation of blood takes place through heart chambers. (3 marks)
The superior vena cava (for upper body) and inferior vena cava (for lower body) receive deoxygenated /impure blood from various part of the body through different veins. This deoxygenated/ impure blood they pour into the right atrium of heart. The blood from right atrium enters the right ventricle through a tricuspid valve, which prevent back flow of blood from ventricle into atrium.
The deoxygenated/ impure blood from right ventricle is forced into pulmonary artery through pulmonary valve. The pulmonary arteries divide into two branches each enters the right and left lungs. In the lungs, the red blood cells (RBCs) release carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen. This oxygenated blood from right and left lungs is collected by four pulmonary veins and poured into left atrium. From left atrium this blood enters into left ventricle through bicuspid valve which prevents back flow of blood into left atrium.This oxygenated blood from left ventricle is forced into the aorta through aortic valve which prevent back flow of blood into left ventricle.
- Give the various functions of medulla oblongata. (03 marks, 1mark for each function The vital centres consisting of group of cells associated with autonomic reflex activity lie in Medulla oblongata. They are,
19
- Cardiac centre– The cardiac centre controls the rate and force of cardiac contraction and blood
- Respiratory centre – The respiratory centre controls the rate and depth of respiration. Nerve impulses pass to the phrenic and intercostal muscles which stimulate the contraction of diaphragm and intercostal muscles, thus initiating
- Vasomotor centre – This controls the diameter of blood vessels especially small arteries and arterioles.
- Reflex centre – When irritating substance are present in stomach or respiratory tract, nerve impulse pass on to the medulla oblongata stimulating the reflex centre which initiate reflex actions like vomiting, sneezing and
(d) Explain retina of eye. (3marks)
- Retina is the innermost layer of the eye. It gets stimulated by the light rays. It is composed of several layers of nerve cell body & the axons. There are light sensitive cells mainly of two types: the rods and
- The entire retina contains about 7 million cones and 75 to 150 million
- Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black-and-white vision, The rods have rhodopsin or visual purple is photosensitive pigment. It gets bleached with light & gets regenerated by vit. A. The rods are present more in the periphery of the
- Cones sensitive to bright light & colour. cone opsins (also known as photopsins or iodopsin) present in cone cells, are used in colour
- The central retina has macula lutea or yellow spot made up of only cone cells. It has central depression called fovea centralis.All the nerve fibres of retina form the optic nerve. The small area of the retina where the optic nerve leave the eye is known as optic disc or blind spot as no light sensitive cells are present here.
20
(e) Define nephritis. Give function of kidney. (Definition 1 mark, any 4 functions 2 marks)
Nephritis: Nephritis refers to inflammation of one or both kidneys due to infection or autoimmune disease.
Functions of kidney are:
- Formation of urine –Each kidney consist of nephron which filter waste product from blood & helps in urine ,
- Maintenance of acid base balance it helps maintaining pH by excretion of H+ ions & reabsorption of HCO3–
- Maintenance of electrolyte balance
- Maintenance of blood pressure. it regulates B.P. by Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone system
- Maintenance of water Balance.it helps in maintaining water balance with the help of
- Formation of erythropoietin hormone for erythropoeisis
(f) Define (3 marks, 1 mark for each definition)
- Mastication: It is the process by which food is chewed and mixed with saliva to form a soft mass or bolus which is swallowed. OR Mastication means chewing process takes place in mouth cavity.
- Chyme: The thick semisolid mass of partially digested food that is passed from the stomach to the
- ii) Digestion: The conversion of complex food ( carbohydrate , proteins & fats) into simpler form (glucose, amino acids & fatty acid) by mechanical breakdown & chemical digestion so that it is easily absorbed into the blood and utilized for energy.
21
Q.6 Solve any four of the following: (16 marks, 4 marks each)
- State eight (8) functions of liver. (0.5 marks for each function)
Functions of liver
- Secretion of bile: Bile salts are helpful in digestion and absorption of fats by its emulsification.
- Glycogenic function: The hepatic cells by the action of enzymes convert glucose into glycogen and it is then stored in the
- Formation of urea: Hepatic cells by the action of the enzyme cause deamination of amino acid, i.e. amine group is set free which forms
- Metabolism of fat: Whenever energy is needed, the saturated stored fat is converted to a form in which it can be used to provide
- Formation of RBCs in foetal
- Destruction of RBCs forming bile pigments and
- Formation of plasma
- Formation of heparin, a natural anticoagulant in the
- Storage of iron and vitamin B
- Maintenance of body temperature: As a number of chemical reactions occur in the liver, heat is generated which is helpful in maintaining body
- Excretion of toxic substances: The toxic substances entering the body through alimentary canal are destroyed in
OR
22
- Carbohydrate metabolism: It helps in maintaining plasma glucose level with the help of insulin &
- Fat metabolism: Stored fat can be converted to a form in which it can be used by the tissue to provide
- Protein metabolism: Deamination of amino -removes nitrogenous portion from amino acid not required for formation of new protein. Urea is formed from the nitrogenous portion which is excreted in urine. Break down of nucleic acids to form uric acid which is excreted in urine. Transamination: Removes the nitrogenous portion of amino acid & attaches it to carbohydrate molecule forming new non-essential amino acid. .
- Synthesis of plasma protein & most blood clotting factors from amino
- Breakdown of RBCs & defense against This is carried out by Kupffer cells.
- Detoxification of drugs & noxious
- Inactivation of hormones
- Production of heat
- Secretion of bile
- Storage of glycogen, iron, copper, & water fat soluble vit-A, D,E, K, soluble vit. Like B12.
(b) What is hepatic portal circulation? Give its importance. (4marks; circulation 3 marks, importance 1 mark)
The portal circulation (3 marks)
In all parts of the body, the venous blood passes from the tissues to the heart by the direct route.
But, in the portal circulation, venous blood from the capillary bed of the abdominal parts, the spleen & the pancreas passes to the liver via the portal vein. The portal vein is formed by union of gastric vein from stomach, superior & inferior mesenteric veins from small and large intestine, splenic vein from spleen & cystic vein from gall bladder. The blood
23
passes through the secondary capillary bed, the hepatic sinusoid in the liver before entering the general circulation via the inferior vena cava.
Importance of portal circulation (1mark)
Blood with the high concentration of nutrients absorbed from the stomach & intestine goes to liver first. In the liver certain modifications takes place including the blood nutrient level. The venous blood then leaves liver via hepatic vein & joins the inferior vena cava.
(c) State functions of Semen and Placenta (4 marks, 2 marks each) Functions of Semen: (2 marks)
- Increase motility and fertility of spermatozoa.
- Semen is slightly alkaline, to neutralize the acidity of
- Prostaglandin present causes contraction of
- It contains nutrients to nourish and support the sperm during their journey through the female reproductive
Functions of placenta: (2 marks)
- To provide the foetus with nourishment and removal of waste material from the
- To act as the foetal lung by providing oxygenation of the fetal blood
- The placenta also acts as a barrier in preventing certain micro-organisms of disease reaching the fetus thus protects the
- The placenta helps the ovaries in the production of estrogen & progesterone hormones necessary for the continuation and maintenance of
24
(d)What is sensory and motor neuron? (1+1 marks). Draw a well labeled diagram of typical neuron (2 marks).
Sensory neuron (1 mark): They carry information from the body to the spinal cord. The impulses may then pass to the brain or to connector neurons of reflex arcs in the spinal cord.
Motor neuron (1 mark): They originate in the brain, spinal cord and autonomic ganglia. They transmit impulses to the effector organs; muscles and glands.
(e) Write the effect of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation on:(4 marks, 2marks each )
- Pupils:(0.5 + 0.5 marks)
Sympathetic stimulation: Dilation of pupils causing mydriasis.
Parasymp. stimulation: Constriction of pupils causing miosis.
(ii) Bronchioles 🙁 0.5+0.5 marks)
Sympathetic stimulation: Bronchodilation allowing greater amount of air to enter the lungs at each inspiration.
Parasymp. stimulation: Bronchoconstriction (Broncho-spasm)
- Blood vessel (1+1 marks) Sympathetic stimulation: Coronary artery: Vasodilation Skeletal blood vessels: Vasodilation
Other blood vessels: Vasoconstriction. Parasympathetic stimulation: Coronary artery: Vasoconstriction Skeletal blood vessels: Vasoconstriction Other blood vessels: Vasodilation
(e) Explain the role of insulin and glucagon in the body. (4 marks, 2 marks each) Role of insulin (3 marks):
Role of insulin
- It increases the uptake of glucose by the
- Increases the conversion of glucose to glycogen in the liver & skeletal
- It increases the uptake of amino acids by the
- It promotes the synthesis of fatty acids & storage of fats in adipose tissue
- decreases
- Prevents breakdown of protein, fat & gluconeogenesis
Role of glucagon (1 mark): Its function is to increase blood sugar level. Whenever the blood sugar level falls below the normal the glycogen stored in the liver is broken down to glucose by the hormone glucagon.
Thus the two hormones help to maintain the blood sugar level constant.
Searches:
pharmacy notes free download, d pharmacy 2nd year notes pdf, d pharmacy 1st year notes in hindi, d pharmacy 1st year notes pharmaceutics, pharm d lecture notes, b pharmacy 2nd year notes, pharmacy notes pdf, pharmacognosy notes for d pharm 1, d pharmacy human anatomy and physiology,