UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS
The following is a brief description of selected unit operations and the operation and validation concerns associated with them. Not all unit operations are discussed, nor are all potential problems addressed. The purpose is to highlight issues that focus on the design, installation, operation, maintenance, and monitoring parameters that facilitate water system validation.
Prefiltration
The purpose of prefiltration—also referred to as initial, coarse, or depth filtration—is to remove solid contaminants down to a size of 7 to 10 µm from the incoming source water supply and protect downstream system components from particulates that can inhibit equipment performance and shorten their effective life. This coarse filtration technology utilizes primarily sieving effects for particle capture and a depth of filtration medium that has a high “dirt load” capacity. Such filtration units are available in a wide range of designs and for various applications. Removal efficiencies and capacities differ significantly, from granular bed filters such as multimedia or sand for larger water systems, to depth cartridges for smaller water systems. Unit and system configurations vary widely in type of filtering media and location in the process. Granular or cartridge prefilters are often situated at or near the head of the water pretreatment system prior to unit operations designed to remove the source water disinfectants. This location, however, does not preclude the need for periodic microbial control because biofilm can still proliferate, although at a slower rate in the presence of source water disinfectants. Design and operational issues that may impact performance of depth filters include channeling of the filtering media, blockage from silt, microbial growth, and filtering-media loss during improper backwashing. Control measures involve pressure and flow monitoring during use and backwashing, sanitizing, and replacing filtering media. An important design concern is sizing of the filter to prevent channeling or media loss resulting from inappropriate water flow rates as well as proper sizing to minimize excessively frequent or infrequent backwashing or cartridge filter replacement.
Activated Carbon
Granular activated carbon beds adsorb low molecular weight organic material and oxidizing additives, such as chlorine and chloramine compounds, removing them from the water. They are used to achieve certain quality attributes and to protect against reaction with downstream stainless steel surfaces, resins, and membranes. The chief operating concerns regarding activated carbon beds include the propensity to support bacteria growth, the potential for hydraulic channeling, the organic adsorption capacity, appropriate water flow rates and contact time, the inability to be regenerated in situ, and the shedding of bacteria, endotoxins, organic chemicals, and fine carbon particles. Control measures may involve monitoring water flow rates and differential pressures, sanitizing with hot water or steam, backwashing, testing for adsorption capacity, and frequent replacement of the carbon bed. If the activated carbon bed is intended for organic reduction, it may also be appropriate to monitor influent and effluent TOC. It is important to note that the use of steam for carbon bed sanitization is often incompletely effective due to steam channeling rather than even permeation through the bed. This phenomenon can usually be avoided by using hot water sanitization. It is also important to note that microbial biofilm development on the surface of the granular carbon particles (as well as on other particles such as found in deionizer beds and even multimedia beds) can cause adjacent bed granules to “stick” together. When large masses of granules are agglomerated in this fashion, normal backwashing and bed fluidization flow parameters may not be sufficient to disperse them, leading to ineffective removal of trapped debris, loose biofilm, and penetration of microbial controlling conditions (as well as regenerant chemicals as in the case of agglomerated deionizer resins). Alternative technologies to activated carbon beds can be used in order to avoid their microbial problems, such as disinfectant-neutralizing chemical additives and regenerable organic scavenging devices. However, these alternatives do not function by the same mechanisms as activated carbon, may not be as effective at removing disinfectants and some organics, and have a different set of operating concerns and control measures that may be nearly as troublesome as activated carbon beds.
Additives
Chemical additives are used in water systems (a) to control microorganisms by use of sanitants such as chlorine compounds and ozone, (b) to enhance the removal of suspended solids by use of flocculating agents, (c) to remove chlorine compounds, (d) to avoid scaling on reverse osmosis membranes, and (e) to adjust pH for more effective removal of carbonate and ammonia compounds by reverse osmosis. These additives do not constitute “added substances” as long as they are either removed by subsequent processing steps or are otherwise absent from the finished water. Control of additives to ensure a continuously effective concentration and subsequent monitoring to ensure their removal should be designed into the system and included in the monitoring program.
Organic Scavengers
Organic scavenging devices use macroreticular weakly basic anion-exchange resins capable of removing organic material and endotoxins from the water. They can be regenerated with appropriate biocidal caustic brine solutions. Operating concerns are associated with organic scavenging capacity, particulate, chemical and microbiological fouling of the reactive resin surface, flow rate, regeneration frequency, and shedding of resin fragments. Control measures include TOC testing of influent and effluent, backwashing, monitoring hydraulic performance, and using downstream filters to remove resin fines.
Softeners
Water softeners may be located either upstream or downstream of disinfectant removal units. They utilize sodium-based cation-exchange resins to remove water-hardness ions, such as calcium and magnesium, that could foul or interfere with the performance of downstream processing equipment such as reverse osmosis membranes, deionization devices, and distillation units. Water softeners can also be used to remove other lower affinity cations, such as the ammonium ion, that may be released from chloramine disinfectants commonly used in drinking water and which might otherwise carryover through other downstream unit operations. If ammonium removal is one of its purposes, the softener must be located downstream of the disinfectant removal operation, which itself may liberate ammonium from neutralized chloramine disinfectants. Water softener resin beds are regenerated with concentrated sodium chloride solution (brine). Concerns include microorganism proliferation, channeling caused by biofilm agglomeration of resin particles, appropriate water flow rates and contact time, ion-exchange capacity, organic and particulate resin fouling, organic leaching from new resins, fracture of the resin beads, resin degradation by excessively chlorinated water, and contamination from the brine solution used for regeneration. Control measures involve recirculation of water during periods of low water use, periodic sanitization of the resin and brine system, use of microbial control devices (e.g., UV light and chlorine), locating the unit upstream of the disinfectant removal step (if used only for softening), appropriate regeneration frequency, effluent chemical monitoring (e.g., hardness ions and possibly ammonium), and downstream filtration to remove resin fines. If a softener is used for ammonium removal from chloramine-containing source water, then capacity, contact time, resin surface fouling, pH, and regeneration frequency are very important.
Deionization
Deionization (DI), and continuous electrodeionization (CEDI) are effective methods of improving the chemical quality attributes of water by removing cations and anions. DI systems have charged resins that require periodic regeneration with an acid and base. Typically, cationic resins are regenerated with either hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, which replace the captured positive ions with hydrogen ions. Anionic resins are regenerated with sodium or potassium hydroxide, which replace captured negative ions with hydroxide ions. Because free endotoxin is negatively charged, there is some removal of endotoxin achieved by the anionic resin. Both regenerant chemicals are biocidal and offer a measure of microbial control. The system can be designed so that the cation and anion resins are in separate or “twin” beds or they can be mixed together to form a mixed bed. Twin beds are easily regenerated but deionize water less efficiently than mixed beds, which have a considerably more complex regeneration process. Rechargeable resin canisters can also be used for this purpose.
[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS
[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS![[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS im](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/PPT-PDF-Pharmaceutical-Water-System-Design-Validation-UNIT-OPERATIONS-CONCERNS.jpg) [PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS
[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS
The CEDI system uses a combination of mixed resin, selectively permeable membranes, and an electric charge, providing continuous flow (product and waste concentrate) and continuous regeneration. Water enters both the resin section and the waste (concentrate) section. As it passes through the resin, it is deionized to become product water. The resin acts as a conductor enabling the electrical potential to drive the captured cations and anions through the resin and appropriate membranes for concentration and removal in the waste water stream. The electrical potential also separates the water in the resin (product) section into hydrogen and hydroxide ions. This permits continuous regeneration of the resin without the need for regenerant additives. However, unlike conventional deionization, CEDI units must start with water that is already partially purified because they generally cannot produce Purified Waterquality when starting with the heavier ion load of unpurified source water.
Concerns for all forms of deionization units include microbial and endotoxin control, chemical additive impact on resins and membranes, and loss, degradation, and fouling of resin. Issues of concern specific to DI units include regeneration frequency and completeness, channeling, caused by biofilm agglomeration of resin particles, organic leaching from new resins, complete resin separation for mixed bed regeneration, and mixing air contamination (mixed beds). Control measures vary but typically include recirculation loops, effluent microbial control by UV light, conductivity monitoring, resin testing, microporous filtration of mixing air, microbial monitoring, frequent regeneration to minimize and control microorganism growth, sizing the equipment for suitable water flow and contact time, and use of elevated temperatures. Internal distributor and regeneration piping for mixed bed units should be configured to ensure that regeneration chemicals contact all internal bed and piping surfaces and resins. Rechargeable canisters can be the source of contamination and should be carefully monitored. Full knowledge of previous resin use, minimum storage time between regeneration and use, and appropriate sanitizing procedures are critical factors ensuring proper performance.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) units employ semipermeable membranes. The “pores” of RO membranes are actually intersegmental spaces among the polymer molecules. They are big enough for permeation of water molecules, but too small to permit passage of hydrated chemical ions. However, many factors including pH, temperature, and differential pressure across the membrane affect the selectivity of this permeation. With the proper controls, RO membranes can achieve chemical, microbial, and endotoxin quality improvement. The process streams consist of supply water, product water (permeate), and wastewater (reject). Depending on source water, pretreatment and system configuration variations and chemical additives may be necessary to achieve desired performance and reliability.
A major factor affecting RO performance is the permeate recovery rate, that is, the amount of the water passing through the membrane compared to the amount rejected. This is influenced by the several factors, but most significantly by the pump pressure. Recoveries of 75% are typical, and can accomplish a 1 to 2 log purification of most impurities. For most feed waters, this is usually not enough to meet Purified Water conductivity specifications. A second pass of this permeate water through another RO stage usually achieves the necessary permeate purity if other factors such as pH and temperature have been appropriately adjusted and the ammonia from chloraminated source water has been previously removed. Increasing recoveries with higher pressures in order to reduce the volume of reject water will lead to reduced permeate purity. If increased pressures are needed over time to achieve the same permeate flow, this is an indication of partial membrane blockage that needs to be corrected before it becomes irreversibly fouled, and expensive membrane replacement is the only option.
Other concerns associated with the design and operation of RO units include membrane materials that are extremely sensitive to sanitizing agents and to particulate, chemical, and microbial membrane fouling; membrane and seal integrity; the passage of dissolved gases, such as carbon dioxide and ammonia; and the volume of wastewater, particularly where water discharge is tightly regulated by local authorities. Failure of membrane or seal integrity will result in product water contamination. Methods of control involve suitable pretreatment of the influent water stream, appropriate membrane material selection, integrity challenges, membrane design and heat tolerance, periodic sanitization, and monitoring of differential pressures, conductivity, microbial levels, and TOC.
The development of RO units that can tolerate sanitizing water temperatures as well as operate efficiently and continuously at elevated temperatures has added greatly to their microbial control and to the avoidance of biofouling. RO units can be used alone or in combination with DI and CEDI units as well as ultrafiltration for operational and quality enhancements.
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is a technology most often employed in pharmaceutical water systems for removing endotoxins from a water stream. It can also use semipermeable membranes, but unlike RO, these typically use polysulfone membranes whose intersegmental “pores” have been purposefully exaggerated during their manufacture by preventing the polymer molecules from reaching their smaller equilibrium proximities to each other. Depending on the level of equilibrium control during their fabrication, membranes with differing molecular weight “cutoffs” can be created such that molecules with molecular weights above these cutoffs ratings are rejected and cannot penetrate the filtration matrix.
Ceramic ultrafilters are another molecular sieving technology. Ceramic ultrafilters are self supporting and extremely durable, backwashable, chemically cleanable, and steam sterilizable. However, they may require higher operating pressures than membrane type ultrafilters.
All ultrafiltration devices work primarily by a molecular sieving principle. Ultrafilters with molecular weight cutoff ratings in the range of 10,000 to 20,000 Da are typically used in water systems for removing endotoxins. This technology may be appropriate as an intermediate or final purification step. Similar to RO, successful performance is dependent upon pretreatment of the water by upstream unit operations.
Issues of concern for ultrafilters include compatibility of membrane material with heat and sanitizing agents, membrane integrity, fouling by particles and microorganisms, and seal integrity. Control measures involve filtration medium selection, sanitization, flow design (dead end vs. tangential), integrity challenges, regular cartridge changes, elevated feed water temperature, and monitoring TOC and differential pressure. Additional flexibility in operation is possible based on the way ultrafiltration units are arranged such as in a parallel or series configurations. Care should be taken to avoid stagnant water conditions that could promote microorganism growth in back-up or standby units.
Charge-Modified Filtration
Charge-modified filters are usually microbially retentive filters that are treated during their manufacture to have a positive charge on their surfaces. Microbial retentive filtration will be described in a subsequent section, but the significant feature of these membranes is their electrostatic surface charge. Such charged filters can reduce endotoxin levels in the fluids passing through them by their adsorption (owing to endotoxin’s negative charge) onto the membrane surfaces. Though ultrafilters are more often employed as a unit operation for endotoxin removal in water systems, charge-modified filters may also have a place in endotoxin removal particularly where available upstream pressures are not sufficient for ultrafiltration and for a single, relatively short term use. Charge-modified filters may be difficult to validate for long-term or large-volume endotoxin retention. Even though their purified standard endotoxin retention can be well characterized, their retention capacity for “natural” endotoxins is difficult to gauge. Nevertheless, utility could be demonstrated and validated as short-term, single-use filters at points of use in water systems that are not designed for endotoxin control or where only an endotoxin “polishing” (removal of only slight or occasional endotoxin levels) is needed. Control and validation concerns include volume and duration of use, flow rate, water conductivity and purity, and constancy and concentration of endotoxin levels being removed. All of these factors may have to be evaluated and challenged prior to using this approach, making this a difficult-to-validate application. Even so, there may still be a possible need for additional backup endotoxin testing both upstream and downstream of the filter.
Microbial-Retentive Filtration
Microbial-retentive membrane filters have experienced an evolution of understanding in the past decade that has caused previously held theoretical retention mechanisms to be reconsidered. These filters have a larger effective “pore size” than ultrafilters and are intended to prevent the passage of microorganisms and similarly sized particles without unduly restricting flow. This type of filtration is widely employed within water systems for filtering the bacteria out of both water and compressed gases as well as for vent filters on tanks and stills and other unit operations. However, the properties of the water system microorganisms seem to challenge a filter’s microbial retention from water with phenomena absent from other aseptic filtration applications, such as filter sterilizing of pharmaceutical formulations prior to packaging. In the latter application, sterilizing grade filters are generally considered to have an assigned rating of 0.2 or 0.22 µm. This rather arbitrary rating is associated with filters that have the ability to retain a high level challenge of a specially prepared inoculum of Brevundimonas (formerly Pseudomonas) diminuta.This is a small microorganism originally isolated decades ago from a product that had been “filter sterilized” using a 0.45-µm rated filter. Further study revealed that a percentage of cells of this microorganism could reproducibly penetrate the 0.45-µm sterilizing filters. Through historic correlation of B. diminuta retaining tighter filters, thought to be twice as good as 0.45-µm filter, assigned ratings of 0.2 or 0.22 µm with their successful use in product solution filter sterilization, both this filter rating and the associated high level B. diminuta challenge have become the current benchmarks for sterilizing filtration. New evidence now suggests that for microbial-retentive filters used for pharmaceutical water, B. diminuta may not be the best model microorganism.
An archaic understanding of microbial retentive filtration would lead one to equate a filter’s rating with the false impression of a simple sieve or screen that absolutely retains particles sized at or above the filter’s rating. A current understanding of the mechanisms involved in microbial retention and the variables that can affect those mechanisms has yielded a far more complex interaction of phenomena than previously understood. A combination of simple sieve retention and surface adsorption are now known to contribute to microbial retention.
The following all interact to create some unusual and surprising retention phenomena for water system microorganisms: the variability in the range and average pore sizes created by the various membrane fabrication processes, the variability of the surface chemistry and three-dimensional structure related to the different polymers used in these filter matrices, and the size and surface properties of the microorganism intended to be retained by the filters. B. diminuta may not the best challenge microorganisms for demonstrating bacterial retention for 0.2- to 0.22-µm rated filters for use in water systems because it appears to be more easily retained by these filters than some water system flora. The well-documented appearance of water system microorganisms on the downstream sides of some 0.2- to 0.22-µm rated filters after a relatively short period of use seems to support that some penetration phenomena are at work. Unknown for certain is if this downstream appearance is caused by a “blow-through” or some other pass-through phenomenon as a result of tiny cells or less cell “stickiness”, or by a “growth through” phenomenon as a result of cells hypothetically replicating their way through the pores to the downstream side. Whatever is the penetration mechanism, 0.2- to 0.22-µm rated membranes may not be the best choice for some water system uses.
Microbial retention success in water systems has been reported with the use of some manufacturers’ filters arbitrarily rated as 0.1 µm. There is general agreement that for a given manufacturer, their 0.1-µm rated filters are tighter than their 0.2- to 0.22-µm rated filters. However, comparably rated filters from different manufacturers in water filtration applications may not perform equivalently owing to the different filter fabrication processes and the nonstandardized microbial retention challenge processes currently used for defining the 0.1-µm filter rating. It should be noted that use of 0.1-µm rated membranes generally results in a sacrifice in flow rate compared to 0.2- to 0.22-µm membranes, so whatever membranes are chosen for a water system appliAcation, the user must verify that the membranes are suitable for their intended application, use period, and use process, including flow rate.
For microbial retentive gas filtrations, the same sieving and adsorptive retention phenomena are at work as in liquid filtration, but the adsorptive phenomenon is enhanced by additional electrostatic interactions between particles and filter matrix. These electrostatic interactions are so strong that particle retention for a given filter rating is significantly more efficient in gas filtration than in water or product solution filtrations. These additional adsorptive interactions render filters rated at 0.2 to 0.22 µm unquestionably suitable for microbial retentive gas filtrations. When microbially retentive filters are used in these applications, the membrane surface is typically hydrophobic (non-wettable by water). A significant area of concern for gas filtration is blockage of tank vents by condensed water vapor, which can cause mechanical damage to the tank. Control measures include electrical or steam tracing and a self-draining orientation of vent filter housings to prevent accumulation of vapor condensate. However, a continuously high filter temperature will take an oxidative toll on polypropylene components of the filter, so sterilization of the unit prior to initial use, and periodically thereafter, as well as regular visual inspections, integrity tests, and changes are recommended control methods.
In water applications, microbial retentive filters may be used downstream of unit operations that tend to release microorganisms or upstream of unit operations that are sensitive to microorganisms. Microbial retentive filters may also be used to filter water feeding the distribution system. It should be noted that regulatory authorities allow the use of microbial retentive filters within distribution systems or even at use points if they have been properly validated and are appropriately maintained. A point-of-use filter should only be intended to “polish” the microbial quality of an otherwise well-maintained system and not to serve as the primary microbial control device. The efficacy of system microbial control measures can only be assessed by sampling the water upstream of the filters. As an added measure of protection, in-line UV lamps, appropriately sized for the flow rate (see Sanitization), may be used just upstream of microbial retentive filters to inactivate microorganisms prior to their capture by the filter. This tandem approach tends to greatly delay potential microbial penetration phenomena and can substantially extend filter service life.
Ultraviolet Light
The use of low-pressure UV lights that emit a 254-nm wavelength for microbial control is discussed under Sanitization, but the application of UV light in chemical purification is also emerging. This 254-nm wavelength is also useful in the destruction of ozone. With intense emissions at wavelengths around 185 nm (as well as at 254 nm), medium pressure UV lights have demonstrated utility in the destruction of the chlorine containing disinfectants used in source water as well as for interim stages of water pretreatment. High intensities of this wavelength alone or in combination with other oxidizing sanitants, such as hydrogen peroxide, have been used to lower TOC levels in recirculating distribution systems. The organics are typically converted to carbon dioxide, which equilibrates to bicarbonate, and incompletely oxidized carboxylic acids, both of which can easily be removed by polishing ion-exchange resins. Areas of concern include adequate UV intensity and residence time, gradual loss of UV emissivity with bulb age, gradual formation of UV-absorbing film at the water contact surface, incomplete photodegradation during unforeseen source water hyperchlorination, release of ammonia from chloramine photodegradation, unapparent UV bulb failure, and conductivity degradation in distribution systems using 185-nm UV lights. Control measures include regular inspection or emissivity alarms to detect bulb failures or film occlusions, regular UV bulb sleeve cleaning and wiping, downstream chlorine detectors, downstream polishing deionizers, and regular (approximately yearly) bulb replacement.
Distillation
Distillation units provide chemical and microbial purification via thermal vaporization, mist elimination, and water vapor condensation. A variety of designs is available including single effect, multiple effect, and vapor compression. The latter two configurations are normally used in larger systems because of their generating capacity and efficiency. Distilled water systems require different feed water controls than required by membrane systems. For distillation, due consideration must be given to prior removal of hardness and silica impurities that may foul or corrode the heat transfer surfaces as well as prior removal of those impurities that could volatize and condense along with the water vapor. In spite of general perceptions, even the best distillation process cannot afford absolute removal of contaminating ions and endotoxin. Most stills are recognized as being able to accomplish at least a 3 to 4 log reduction in these impurity concentrations. Areas of concern include carry-over of volatile organic impurities such as trihalomethanes (see Source and Feed Water Considerations) and gaseous impurities such as ammonia and carbon dioxide, faulty mist elimination, evaporator flooding, inadequate blowdown, stagnant water in condensers and evaporators, pump and compressor seal design, pinhole evaporator and condenser leaks, and conductivity (quality) variations during start-up and operation.
Methods of control may involve preliminary decarbonation steps to remove both dissolved carbon dioxide and other volatile or noncondensable impurities; reliable mist elimination to minimize feedwater droplet entrainment; visual or automated high water level indication to detect boiler flooding and boil over; use of sanitary pumps and compressors to minimize microbial and lubricant contamination of feedwater and condensate; proper drainage during inactive periods to minimize microbial growth and accumulation of associated endotoxin in boiler water; blow down control to limit the impurity concentration effect in the boiler to manageable levels; on-line conductivity sensing with automated diversion to waste to prevent unacceptable water upon still startup or still malfunction from getting into the finished water distribute system; and periodic integrity testing for pinhole leaks to routinely assure condensate is not compromised by nonvolatized source water contaminants.
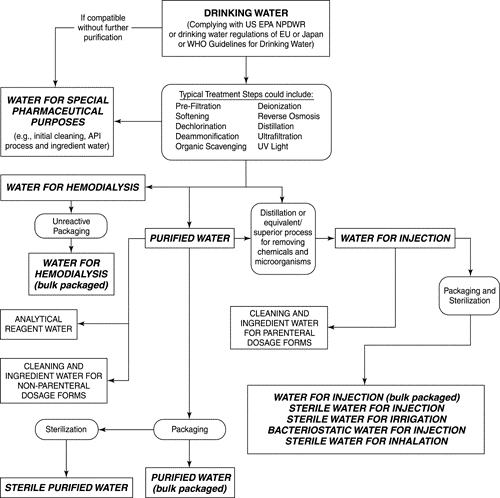
Storage Tanks
Storage tanks are included in water distribution systems to optimize processing equipment capacity. Storage also allows for routine maintenance within the pretreatment train while maintaining continuous supply to meet manufacturing needs. Design and operation considerations are needed to prevent or minimize the development of biofilm, to minimize corrosion, to aid in the use of chemical sanitization of the tanks, and to safeguard mechanical integrity. These considerations may include using closed tanks with smooth interiors, the ability to spray the tank headspace using sprayballs on recirculating loop returns, and the use of heated, jacketed/insulated tanks. This minimizes corrosion and biofilm development and aids in thermal and chemical sanitization. Storage tanks require venting to compensate for the dynamics of changing water levels. This can be accomplished with a properly oriented and heat-traced filter housing fitted with a hydrophobic microbial retentive membrane filter affixed to an atmospheric vent. Alternatively, an automatic membrane-filtered compressed gas blanketing system may be used. In both cases, rupture disks equipped with a rupture alarm device should be used as a further safeguard for the mechanical integrity of the tank. Areas of concern include microbial growth or corrosion due to irregular or incomplete sanitization and microbial contamination from unalarmed rupture disk failures caused by condensate-occluded vent filters.
Distribution Systems
Distribution system configuration should allow for the continuous flow of water in the piping by means of recirculation. Use of nonrecirculating, dead-end, or one-way systems or system segments should be avoided whenever possible. If not possible, these systems should be periodically flushed and more closely monitored. Experience has shown that continuously recirculated systems are easier to maintain. Pumps should be designed to deliver fully turbulent flow conditions to facilitate thorough heat distribution (for hot water sanitized systems) as well as thorough chemical sanitant distribution. Turbulent flow also appear to either retard the development of biofilms or reduce the tendency of those biofilms to shed bacteria into the water. If redundant pumps are used, they should be configured and used to avoid microbial contamination of the system.
Components and distribution lines should be sloped and fitted with drain points so that the system can be completely drained. In stainless steel distribution systems where the water is circulated at a high temperature, dead legs and low-flow conditions should be avoided, and valved tie-in points should have length-to-diameter ratios of six or less. If constructed of heat tolerant plastic, this ratio should be even less to avoid cool points where biofilm development could occur. In ambient temperature distribution systems, particular care should be exercised to avoid or minimize dead leg ratios of any size and provide for complete drainage. If the system is intended to be steam sanitized, careful sloping and low-point drainage is crucial to condensate removal and sanitization success. If drainage of components or distribution lines is intended as a microbial control strategy, they should also be configured to be completely dried using dry compressed air (or nitrogen if appropriate employee safety measures are used). Drained but still moist surfaces will still support microbial proliferation. Water exiting from the distribution system should not be returned to the system without first passing through all or a portion of the purification train.
The distribution design should include the placement of sampling valves in the storage tank and at other locations, such as in the return line of the recirculating water system. Where feasible, the primary sampling sites for water should be the valves that deliver water to the points of use. Direct connections to processes or auxiliary equipment should be designed to prevent reverse flow into the controlled water system. Hoses and heat exchangers that are attached to points of use in order to deliver water for a particular use must not chemically or microbiologically degrade the water quality. The distribution system should permit sanitization for microorganism control. The system may be continuously operated at sanitizing conditions or sanitized periodically.
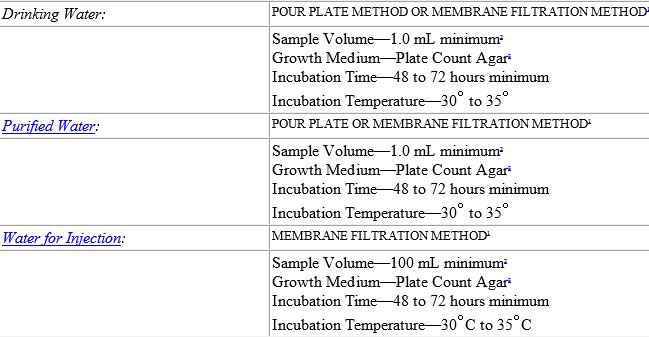
Source : USP
Expert Committee : (PW05) Pharmaceutical Waters 05
USP29–NF24 Page 3056
Pharmacopeial Forum : Volume No. 30(5) Page 1744
Pharmaceutical Water System Ppt,
Pharmaceutical Water Systems,
Purified Water Specification As Per Usp,
Pharmaceutical Water System Design Operation And Validation Pdf,
pharmaceutical water system design operation and validation,
pharmaceutical water system ppt – What is Pharmaceutical water,
purified water & Water for Injection SOP as per usp,
Pharmaceutical Water Systems: Storage & Distribution Systems,
pharmaceutical water system : Inspection of Pharmaceutical water systems,
pharmaceutical water Production : Water purification systems,
Pharmaceutical Water Systems: Types: Water quality specifications,
Pharmaceutical Water System: principles for pharmaceutical water systems


![[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Validation - IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/PPT-PDF-Pharmaceutical-Water-System-Validation-IDENTIFICATION-OF-MICROORGANISMS.jpg)
![[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -UNIT OPERATIONS CONCERNS im](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/PPT-PDF-Pharmaceutical-Water-System-Design-Validation-UNIT-OPERATIONS-CONCERNS.jpg)
![[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation -SAMPLING CONSIDERATIONS](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/PPT-PDF-Pharmaceutical-Water-System-Design-Validation-SAMPLING-CONSIDERATIONS.jpg)
![[PPT PDF] Pharmaceutical Water System Design Validation - Microbial Testing of Water](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/PPT-PDF-Pharmaceutical-Water-System-Design-Validation-Microbial-Testing-of-Water.jpg)

![Pharmaceutical Water Systems Pharmaceutical Water Storage & Distribution Systems [PDF PPT]](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Pharmaceutical-Water-Systems-Pharmaceutical-Water-Storage-Distribution-Systems-PDF-PPT.jpg)
![M Pharmacy Parmaceutics Project APPROACHES TO COLON-SPECIFIC DRUG DELIVERY [Ceutics]](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/M-Pharmacy-Parmaceutics-Project-APPROACHES-TO-COLON-SPECIFIC-DRUG-DELIVERY-Ceutics.png)
![APPROACHES TO COLON-SPECIFIC DRUG DELIVERY [Ceutics notes]](https://pharmawiki.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/APPROACHES-TO-COLON-SPECIFIC-DRUG-DELIVERY-Ceutics-notes.png)